Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times


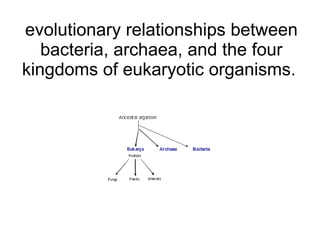






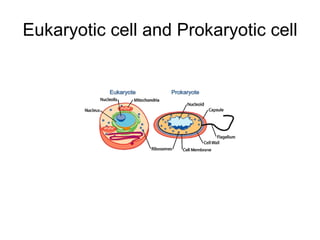

All living things are made up of cells that can be divided into two categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler with no membrane-bound organelles and a single circular chromosome, while eukaryotic cells are more complex with membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and multiple linear chromosomes surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are in their size, structure, organelles, and genetic material.










