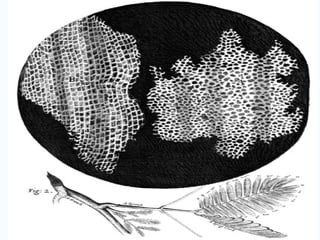
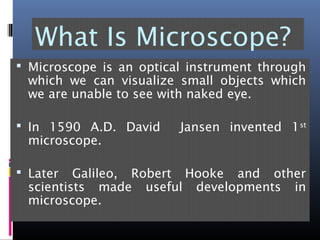
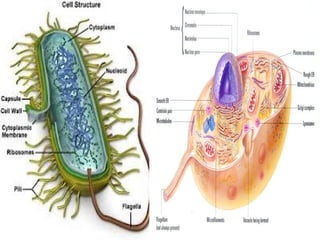
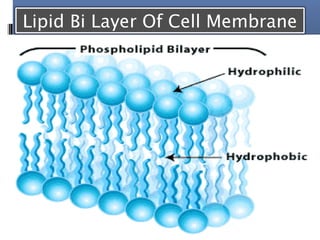
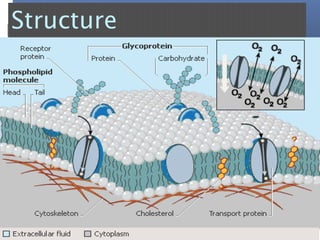
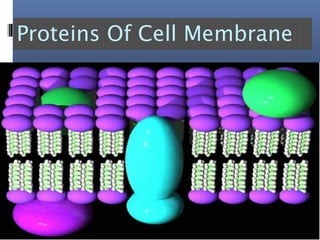
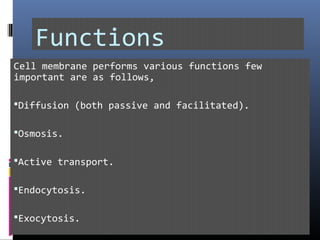
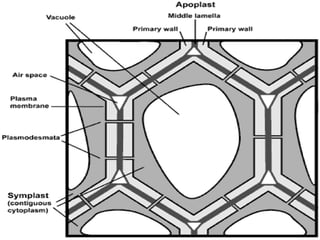
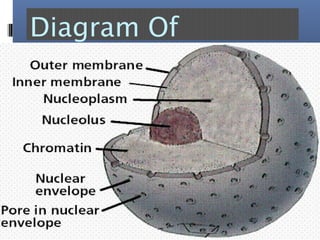
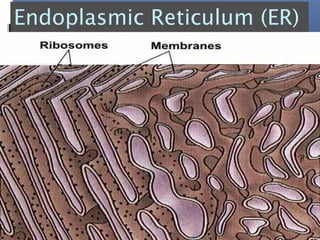
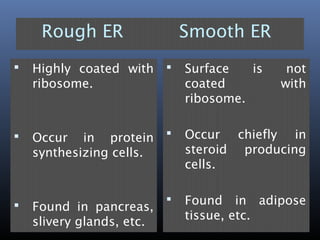
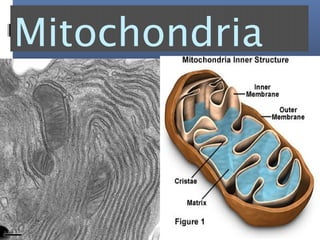
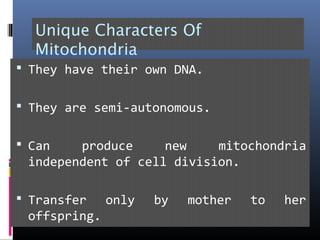
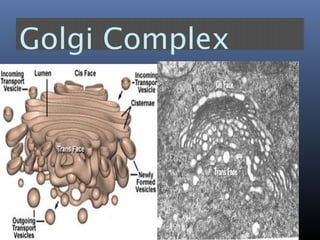
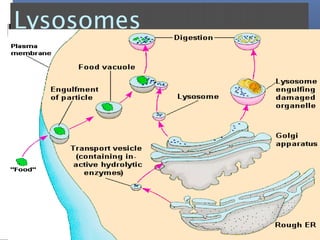
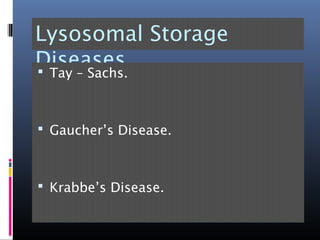
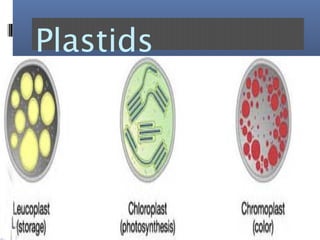
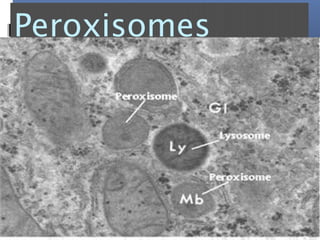
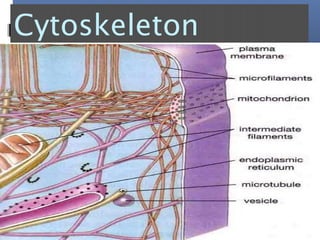
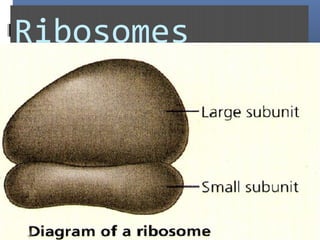
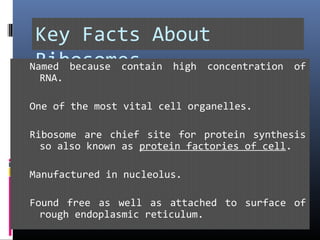
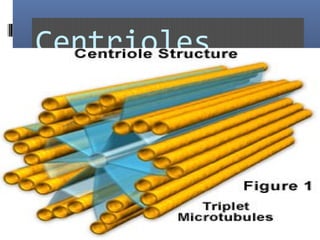
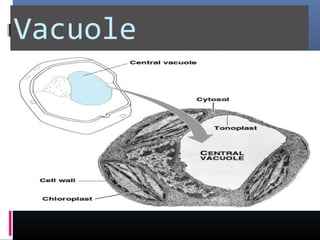
The document provides an overview of cell biology, detailing the discovery of cells, the development of cell theory, and the structure and function of various cellular components such as prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, membranes, organelles, and organelle functions. It covers significant historical milestones in microscopy, cytoplasmic organelles like mitochondria, Golgi complex, and lysosomes, and discusses the differences between plant and animal cells. Additionally, it highlights cell fractionation, the cytoskeleton, and the significance of various organelles and their contributions to cellular function.