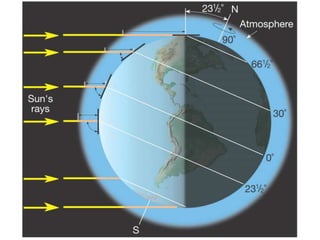
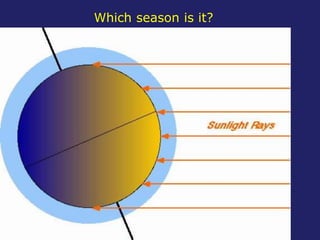
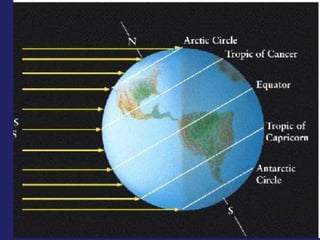
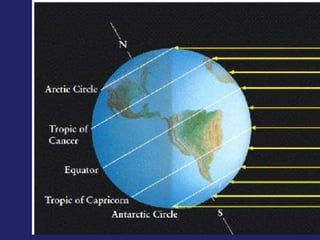
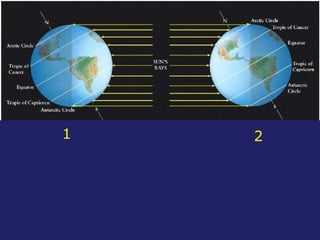
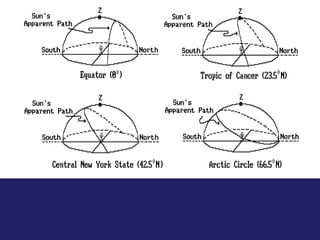
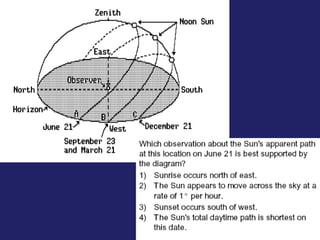
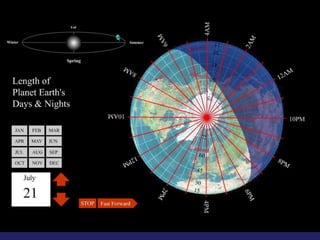
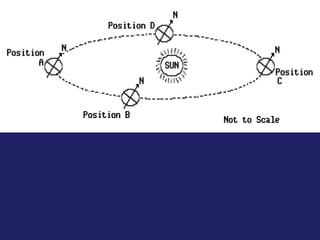
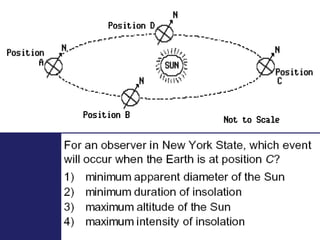
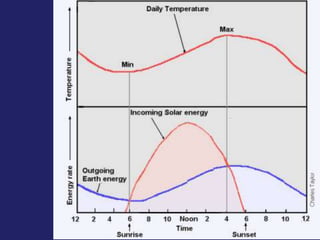
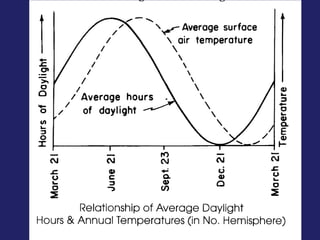
Insolation refers to incoming solar radiation or sunlight. The sun is the primary source of electromagnetic energy for the Earth. The intensity and angle of insolation determine how strong sunlight is, with the highest angle being at noon. Insolation duration varies by latitude and season, affecting hours of daylight. Black, rough surfaces absorb sunlight best while white, smooth surfaces reflect it most. As insolation increases, temperature increases, though temperature peaks about a month after the summer solstice due to lag effects. Seasons are caused by the tilt of Earth's axis and its revolution around the sun.