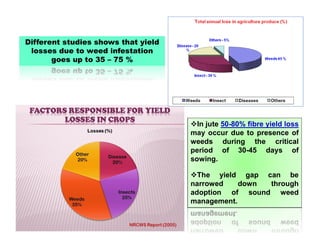
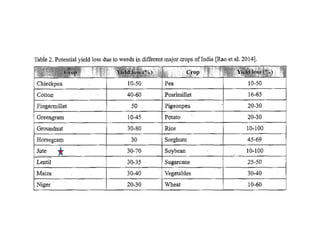
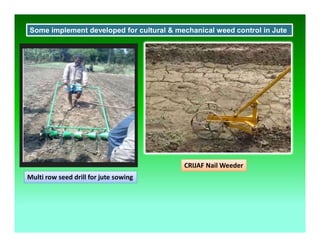
This document discusses weed management in jute crops. Weeds can cause 35-70% yield losses in jute. Integrated weed management approaches are recommended, including the use of pre-emergence herbicides like butachlor followed by post-emergence herbicides like quizalofop-ethyl and one manual weeding. Proper weed control is crucial during the first 30-45 days after sowing, which is the critical period for weed growth in jute. Both cultural methods like intercropping and line sowing as well as herbicides can help manage weeds in jute fields.