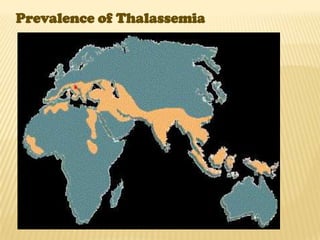
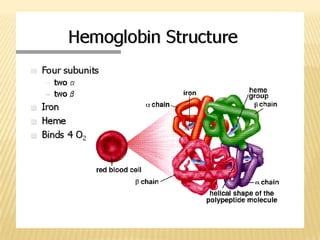
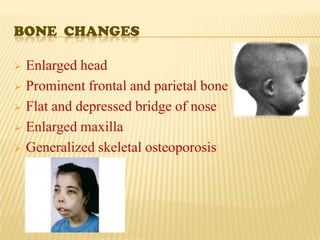
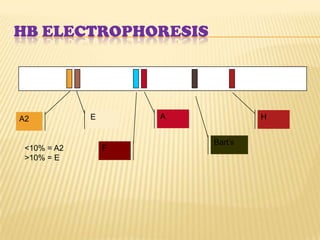
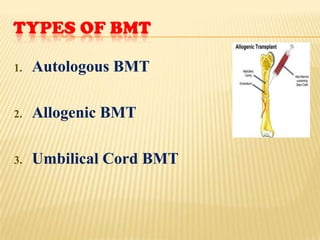
This document discusses thalassemia, an inherited blood disorder characterized by reduced or absent hemoglobin. There are two main types: alpha thalassemia affects hemoglobin production; beta thalassemia has four forms ranging from mild (trait) to severe (major). Symptoms include anemia, fatigue, bone changes. Treatment involves blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and potentially splenectomy or bone marrow transplant.