This document discusses thalassemia, specifically alpha and beta thalassemia. It describes the genetics, pathophysiology, clinical presentations, and laboratory diagnosis of the different types. The main points are:
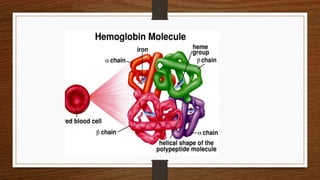
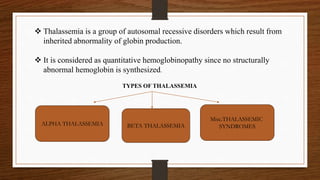
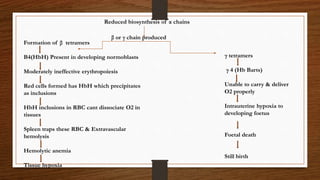
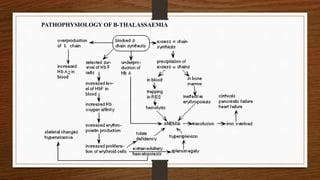
1) Thalassemia results from inherited abnormalities in globin chain production, causing excess unpaired chains. Alpha thalassemia affects alpha chain production, while beta thalassemia affects beta chain production.
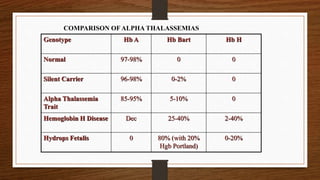
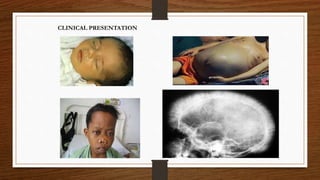
2) There are different clinical syndromes for each type depending on the severity of the genetic mutation, ranging from silent carriers to severe anemia requiring transfusions.
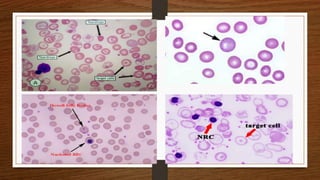
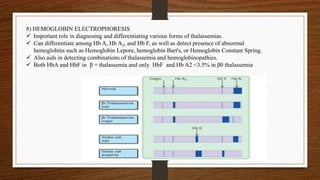
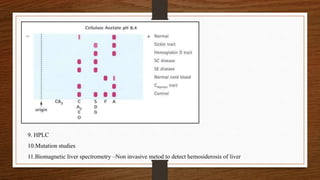
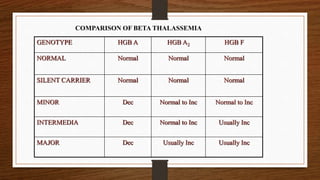
3) Laboratory testing helps diagnose and classify the specific type of thalassemia based on hemoglobin electrophoresis