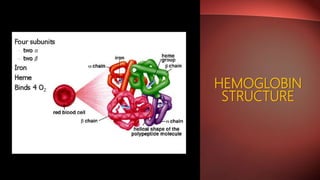
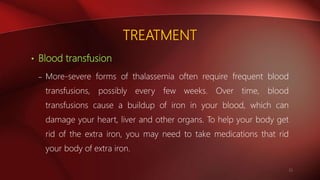
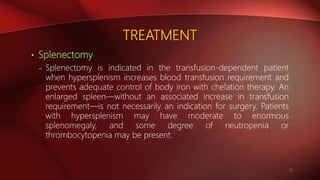
Thalassemia is a hereditary blood disorder characterized by defective hemoglobin production, leading to two main types: alpha and beta thalassemia. Beta thalassemia, often stemming from mutations on chromosome 11, varies in severity from minor forms with mild anemia to major forms causing severe complications and requiring regular blood transfusions. Treatment options include regular transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and in select cases, bone marrow transplantation.