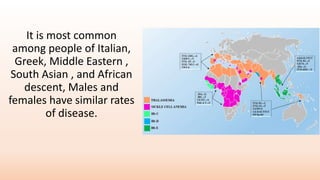
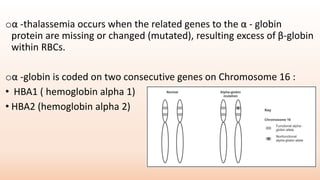
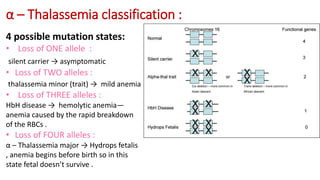
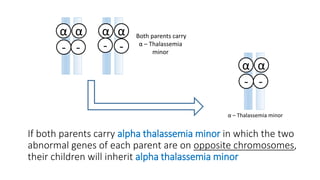
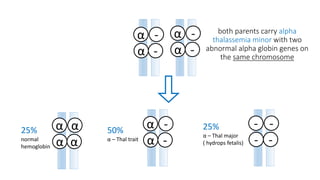
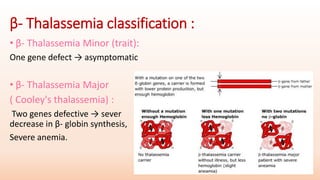
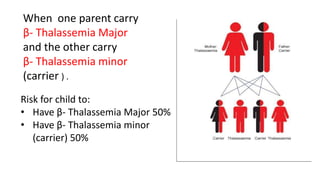
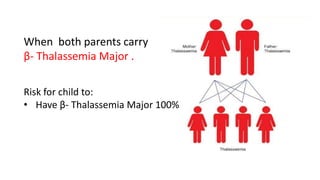
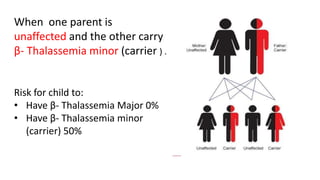
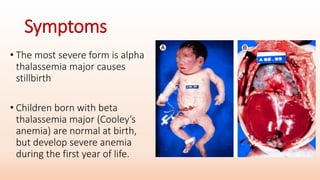
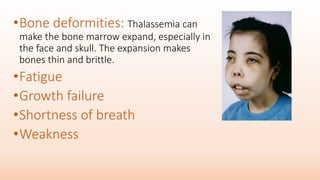
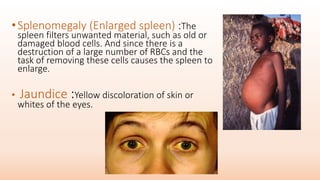
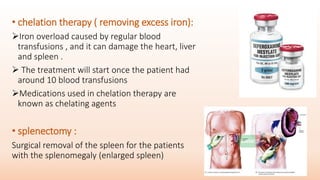
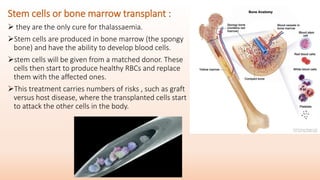
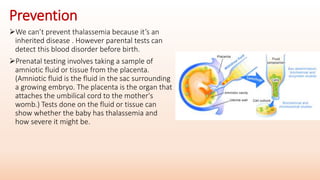
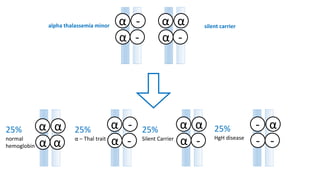
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder that results in abnormal hemoglobin formation and excessive red blood cell destruction, leading to anemia. There are two main types: alpha thalassemia affects genes on chromosome 16 and causes excess beta globin, while beta thalassemia affects the gene on chromosome 11 and causes excess alpha globin. Symptoms include fatigue, growth issues, breathing problems, and enlarged spleen. Treatment involves regular blood transfusions to address anemia, along with chelation therapy to remove excess iron that can damage organs. For severe cases, a bone marrow transplant may potentially cure the condition.