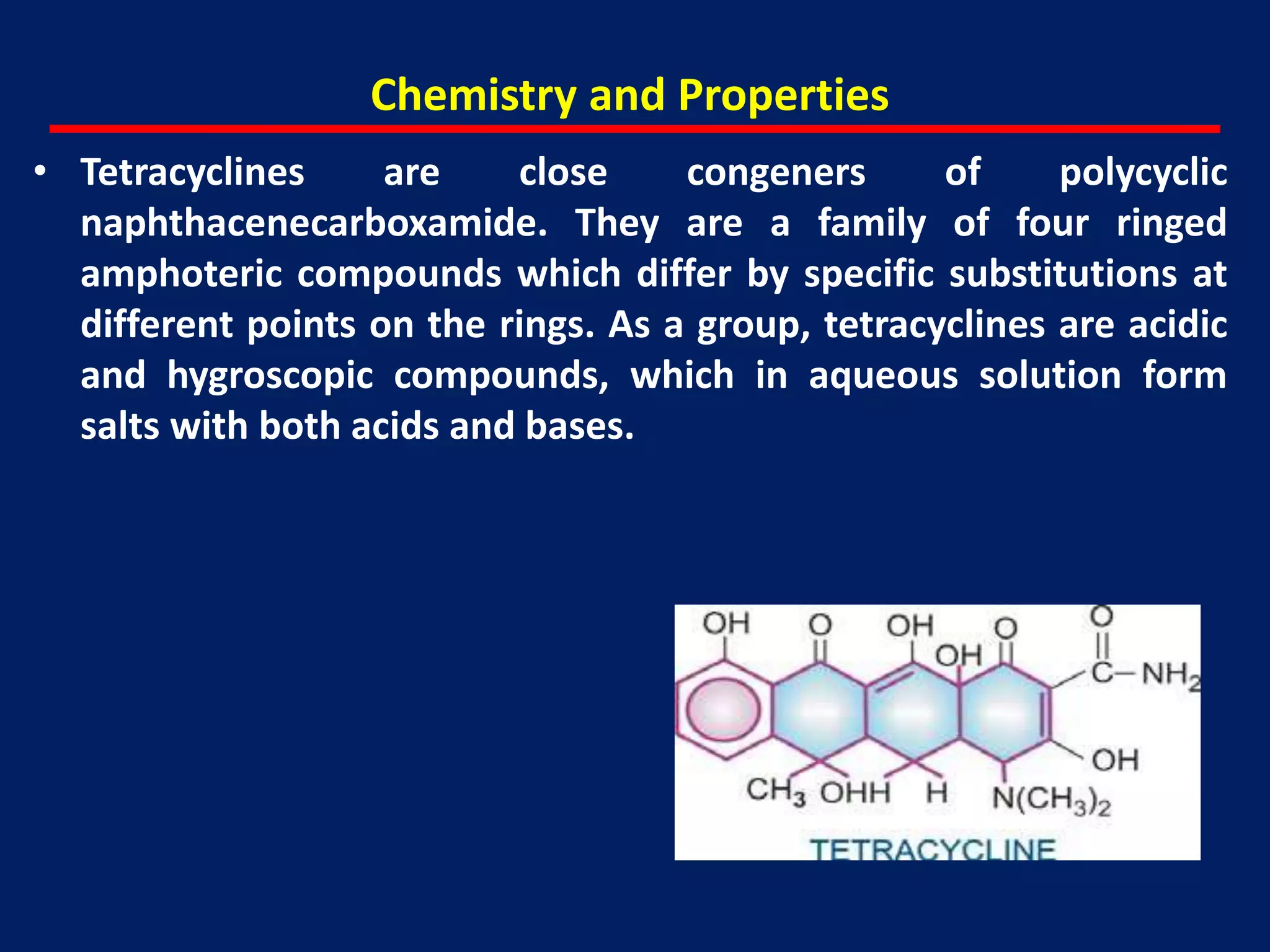
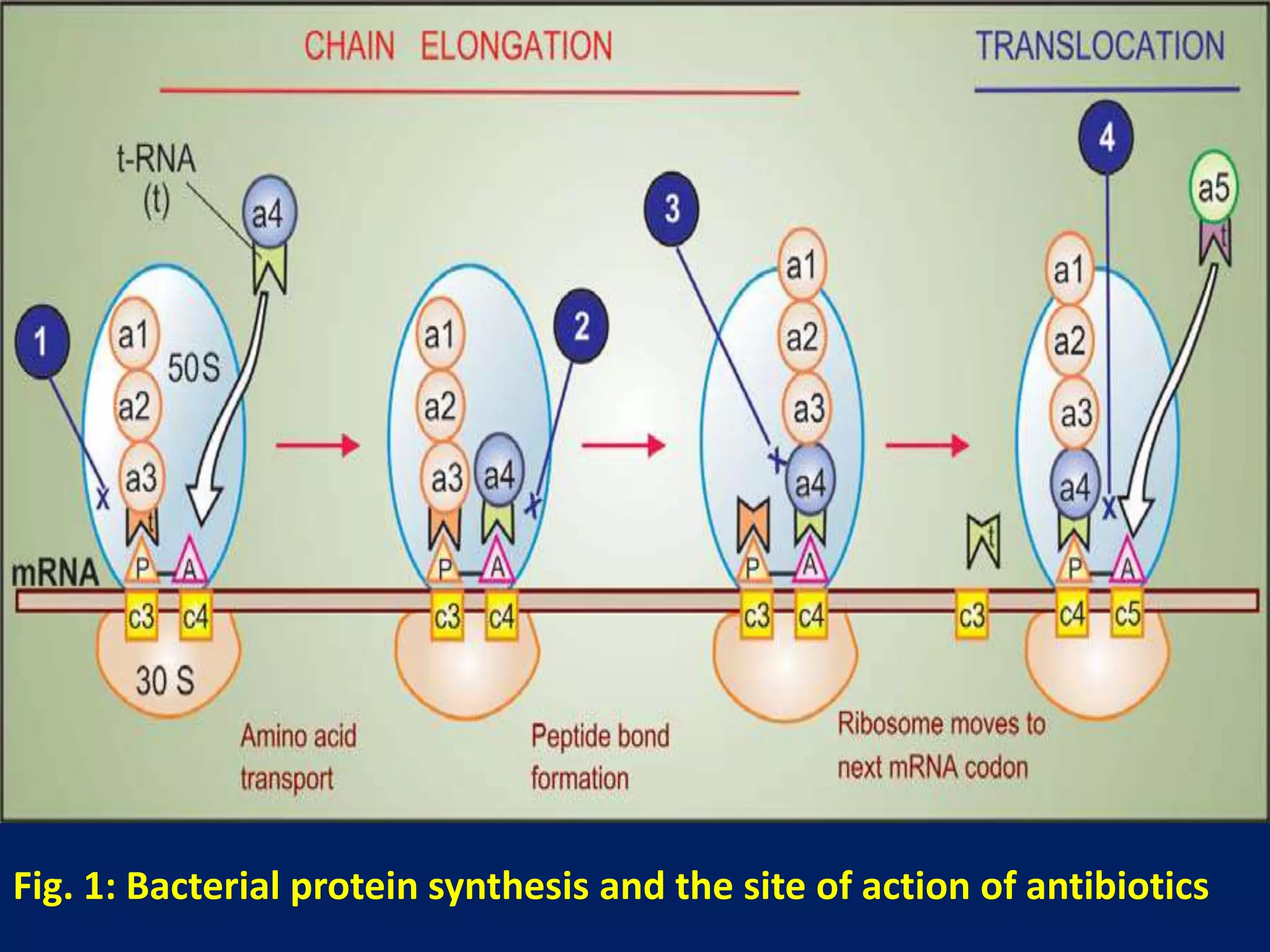
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotics derived from soil actinomycetes. They inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial ribosome. While tetracycline use has declined due to resistance, some remain useful for specific infections. Tetracyclines are classified based on duration of action and include short, intermediate, and long-acting drugs. Adverse effects include gastrointestinal upset, tooth staining in children, and hypersensitivity reactions.