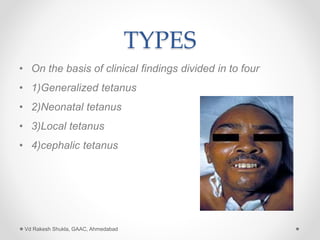
Tetanus is an acute infectious disease caused by toxins produced by Clostridium tetani bacteria. The bacteria typically enters the body through a wound and produces a neurotoxin called tetanospasmin that causes painful muscle spasms. There are four main types of tetanus - generalized, local, cephalic, and neonatal. Symptoms include muscle rigidity, lockjaw, and painful spasms. Treatment involves wound cleaning, antitoxins to neutralize circulating toxins, antibiotics, and managing symptoms. Prevention focuses on active immunization with booster shots every 10 years and proper wound care.