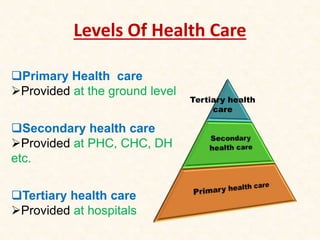
The document discusses the concepts of health, illness, and healthcare. It defines health as a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, not just the absence of disease. Illness is defined as a diminished state of functioning. Healthcare is described as more than just medical care, involving public services to promote, maintain, monitor, and restore health. The document then outlines the three levels of healthcare - primary, secondary, and tertiary - provided at different facilities. It focuses on the principles and goals of primary healthcare as outlined at the Alma-Ata International Conference in 1977, which established primary healthcare as the path to achieving "Health for All by 2000" through making essential care universally accessible.