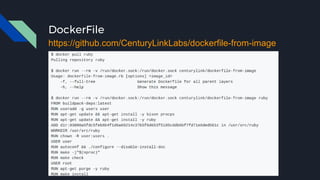
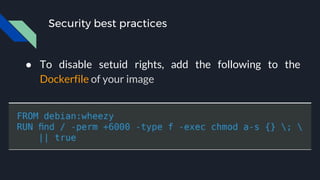
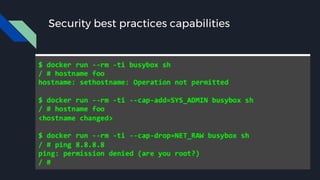
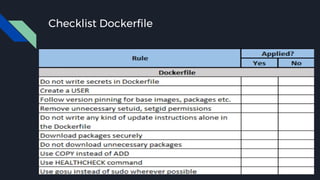
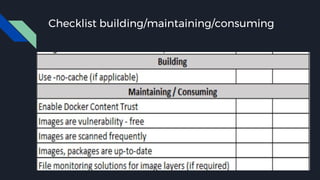
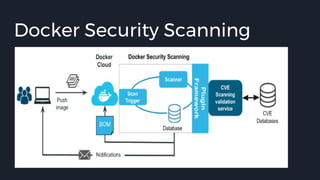
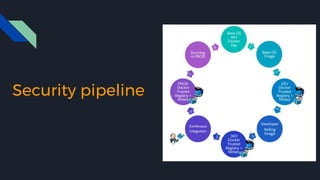
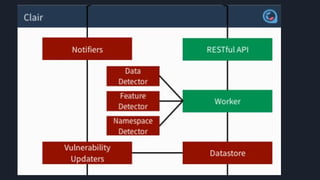
This document discusses tools and best practices for auditing Docker images for security. It begins with an introduction to Docker security concepts like namespaces, cgroups, and capabilities. It then discusses tools like Docker Security Scanning, Clair, Docker Bench Security, and Lynis that can be used to audit images. The document provides checklists for building secure Dockerfiles and consuming images. It concludes with recommendations around signing images, pinning dependencies, and using content trust and least privilege configurations.

























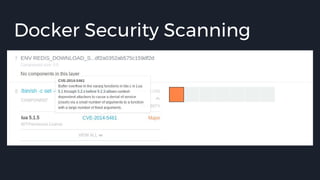






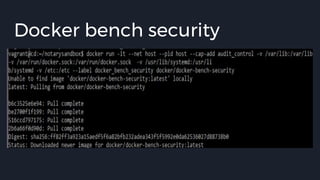

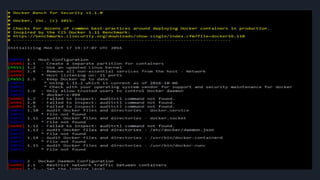
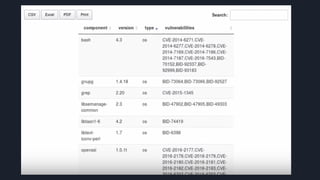
![Docker bench security
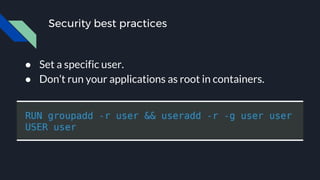
● The Docker daemon configuration
● [WARN] 2.1- Restrict network traffic between containers
● [WARN] 4.1 - Create a user for the container
[WARN] * Running as root:
● [WARN] 5.4 - Restrict Linux Kernel Capabilities within containers
[WARN] * Capabilities added: CapAdd=[audit_control]
● [WARN] 5.13 - Mount container's root filesystem as readonly
[WARN] * Container running with root FS mounted R/W:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-170819010708/85/Testing-Docker-Images-Security-45-320.jpg)