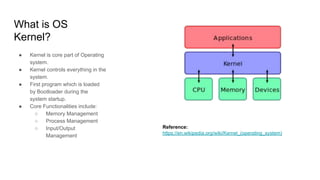
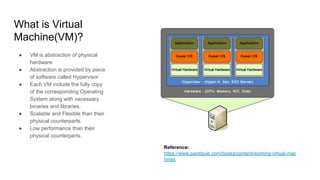
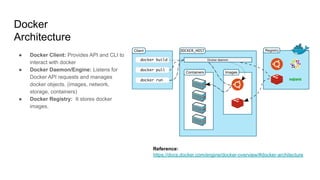
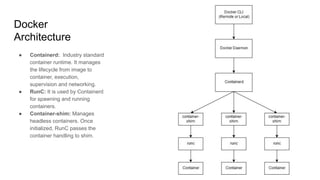
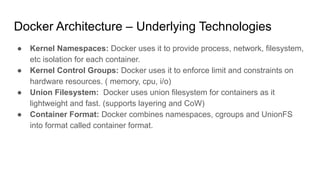
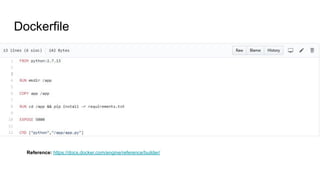
The document provides an overview of Docker fundamentals, including what Docker is, its architecture, common operations, and advantages. It begins by explaining that Docker is a container technology that packages code and dependencies together. Containers run atop the same OS kernel and utilize fewer system resources than virtual machines. The document then describes Docker's client-server architecture and underlying technologies like namespaces and cgroups that enable isolation. It also outlines common Docker commands and explains that Dockerfiles define container configurations.