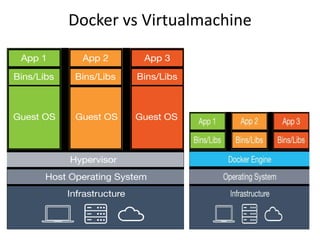
Docker allows developers to package applications with dependencies into standardized units for development and deployment. It provides lightweight containers that run applications securely isolated from the host system and other containers. Key Docker components include images, which are read-only templates used to create and deploy containers as executable instances of the packaged application.