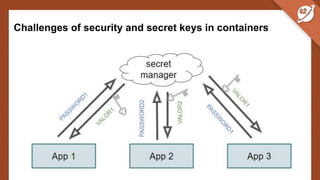
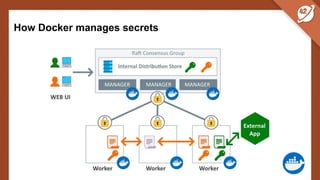
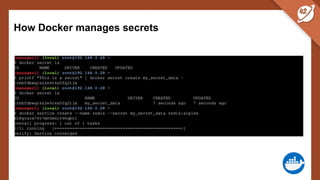
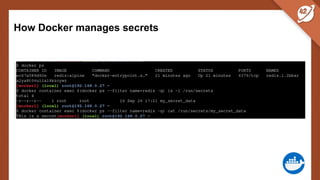
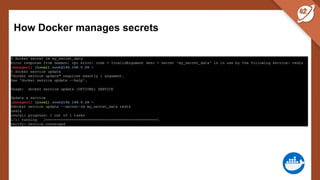
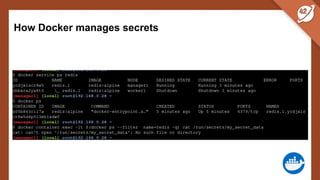
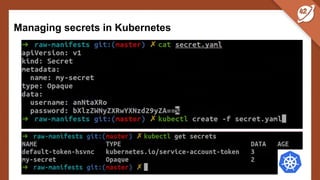
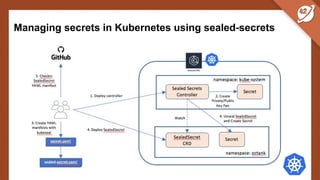
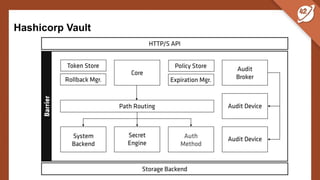
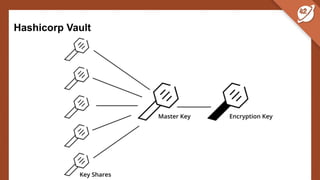
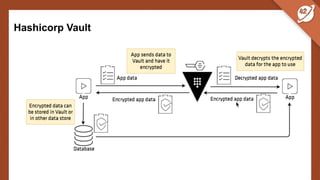
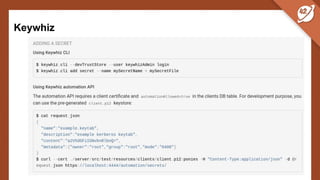
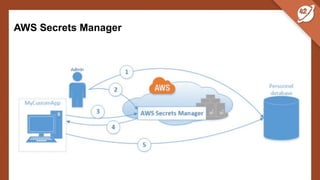
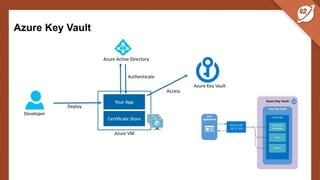
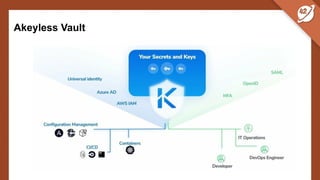
The document discusses the challenges and best practices of managing secret keys in Docker containers and Kubernetes, emphasizing the importance of securely storing sensitive data like passwords and SSH keys. It outlines methods for managing secrets in Docker, including the use of Docker Swarm and Docker Compose, and in Kubernetes through volumes and sealed-secrets. Additionally, it explores other tools for distributing secrets, such as HashiCorp Vault and AWS Secrets Manager, reinforcing the critical role of secrets in container architectures to maintain separation between code and configuration.