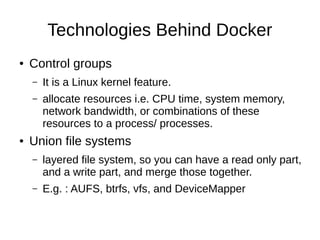
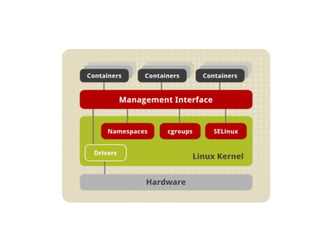
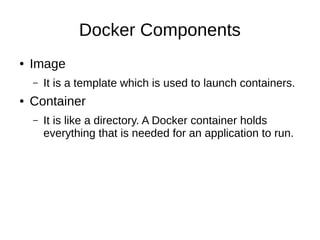
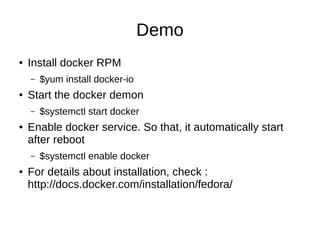
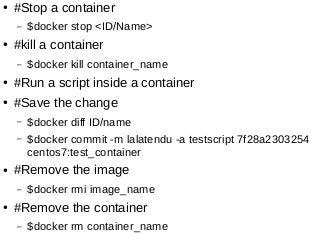
This document introduces Docker, a lightweight container virtualization platform. It discusses how Docker uses Linux kernel features like namespaces and control groups to provide isolation similar to virtual machines but with less overhead. Docker images act as templates to launch containers which contain all dependencies for running applications. The document demonstrates how to install Docker, run containers from images, and manage images and containers. It explains key Docker components like images, containers, registries and repositories. Finally, it encourages getting involved in open source Docker projects.