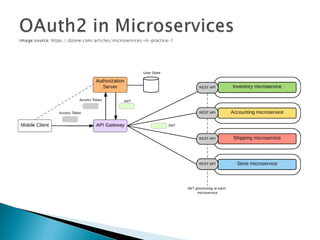
This document discusses container security and provides information on various related topics. It begins with an overview of container security risks such as escapes and application vulnerabilities. It then covers security controls for containers like namespaces, control groups, and capabilities. Next, it discusses access control models and Linux security modules like SELinux and AppArmor that can provide container isolation. The document concludes with some third-party security offerings and emerging technologies that aim to enhance container security.

















![onboot:
- name: dhcpcd
image: linuxkit/dhcpcd:<hash>
command: ["/sbin/dhcpcd", "--nobackground", "-f", "/dhcpcd.conf", "-1"]
- name: wg
image: linuxkit/ip:<hash>
net: new
binds:
- /etc/wireguard:/etc/wireguard
command: ["sh", "-c", "ip link set dev wg0 up; ip address add dev wg0 192.168.2.1 peer 192.168.2.2; wg setconf wg0 /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf; wg show wg0"]
runtime:
interfaces:
- name: wg0
add: wireguard
createInRoot: true
bindNS:
net: /run/netns/wg
services:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:alpine
net: /run/netns/wg
capabilities:
- CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE
- CAP_CHOWN
- CAP_SETUID
- CAP_SETGID
- CAP_DAC_OVERRIDE
Sample LinuxKit YAML File](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/containersecurity-180419062734/85/Container-security-25-320.jpg)