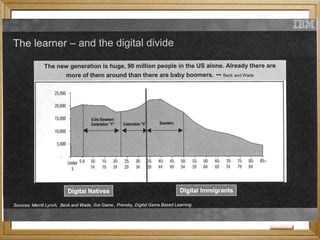
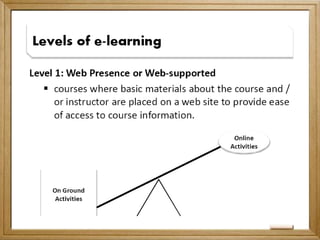
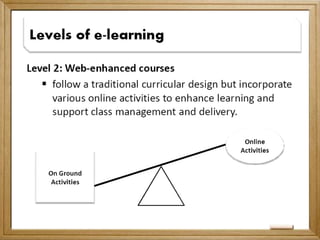
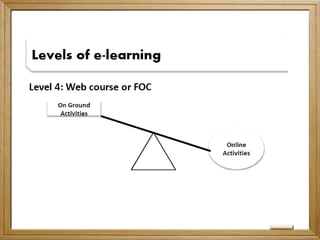
This document provides an overview of the evolution of e-learning in the Philippines through four generations:
1) First generation used radio broadcasting to educate rural communities.
2) Second generation saw universities offer graduate programs through print-based distance learning.
3) Third generation combined ICT, audio/video, and flexible learning opportunities.
4) Current fourth generation fully integrates technology through e-learning, m-learning, and u-learning in schools.