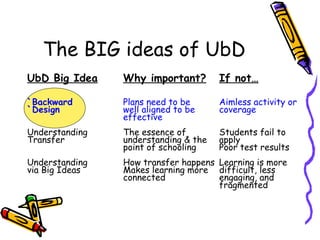
The document emphasizes the importance of backward design in educational planning, stating that effective teaching focuses on achieving clear intellectual goals rather than merely covering content or engaging in activities. It discusses the concept of transfer of learning, where students must apply knowledge in new contexts, and stresses that understanding big ideas is crucial for meaningful learning. Additionally, it highlights common frustrations educators face when students struggle to recall or apply what they have learned, advocating for a more focused approach to teaching that prioritizes deep understanding and real-world application.