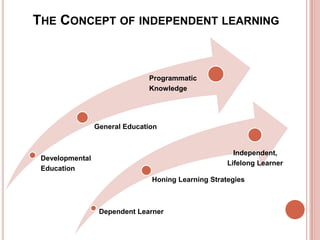
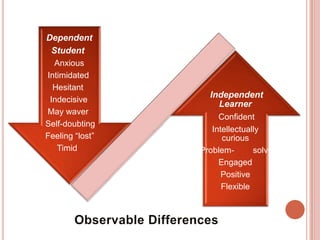
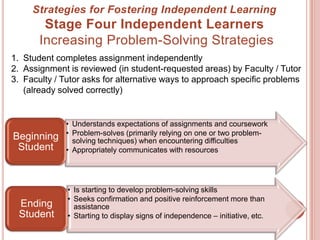
The document discusses the concept of independent learning, its significance in education, and various strategies to foster it in students. It provides insights into observable differences between dependent and independent learners, levels of learning independence, and methods for measuring and increasing independence in the classroom. Additionally, it outlines learning objectives that support independent learning and highlights the importance of problem-solving and self-efficacy among students.









![LEARNING OBJECTIVES THAT
LEAD TO INDEPENDENT LEARNING
Concept-Based
(addresses a long-term need)
Skill-Specific
(addresses a course need)
Assignment-Specific
(addresses an immediate [homework] need)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-jonmladic-pearsonfosteringanindependentlearner-120430133105-phpapp02/85/Fostering-Independent-Learning-13-320.jpg)