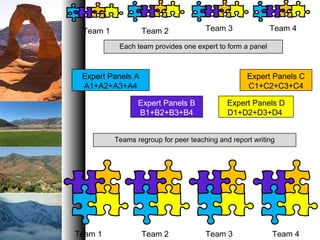
This document discusses various educational methods and instructional techniques. It begins by asking about different instructional methods the reader has been exposed to in high school, college, and non-formal settings. Several analogies are provided that compare teaching to fishing using different lures for different fish, and teaching to music where different instructional methods together become amazing. The document then discusses selecting and using a variety of instructional methods, defining methods of instruction, and factors to consider. A number of teaching methods are identified, such as lecture, case study, group discussion, and field trips. The document provides exercises applying problem-solving techniques and the jigsaw method to integrate reading, speaking, listening and writing skills.