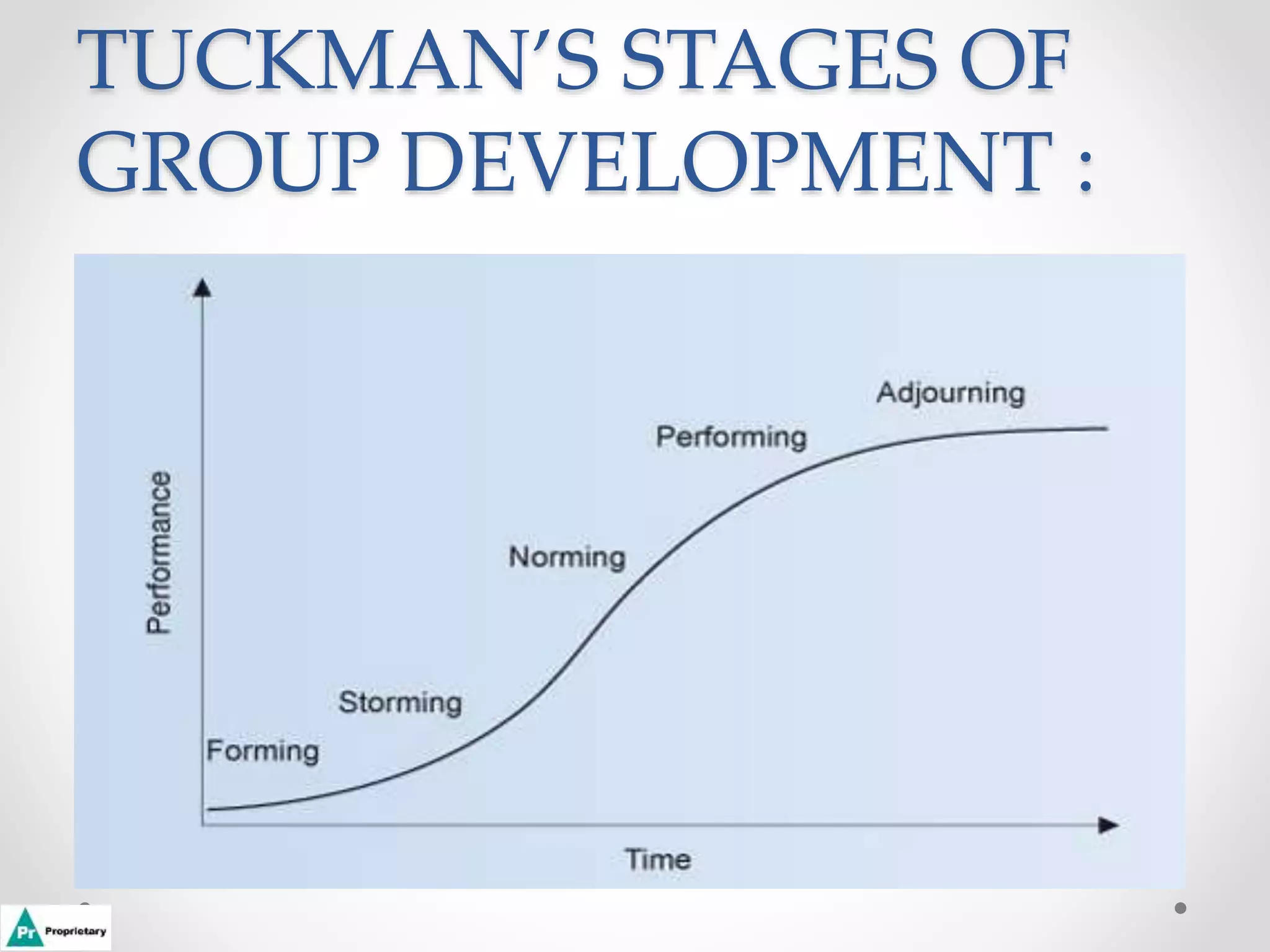
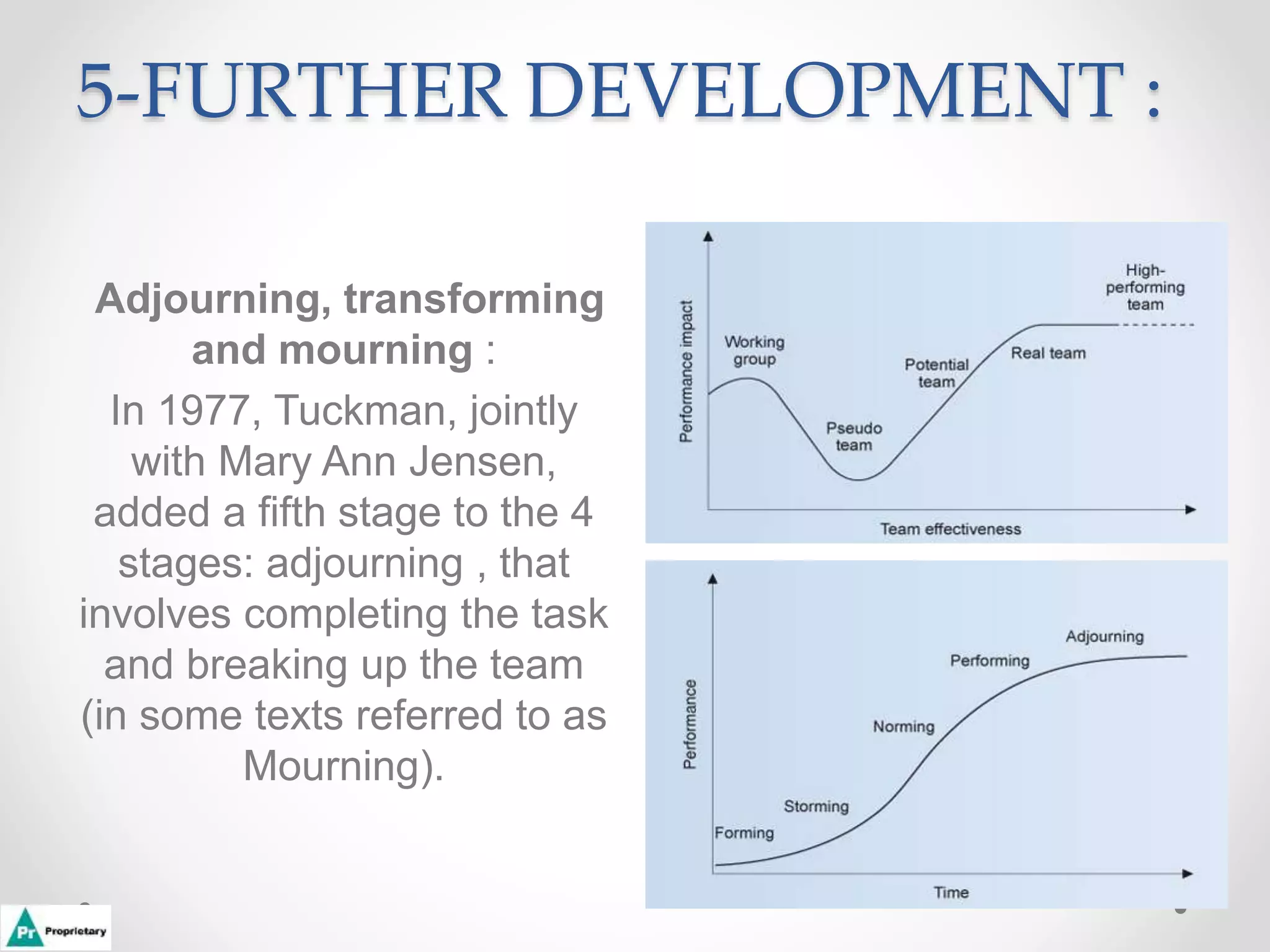
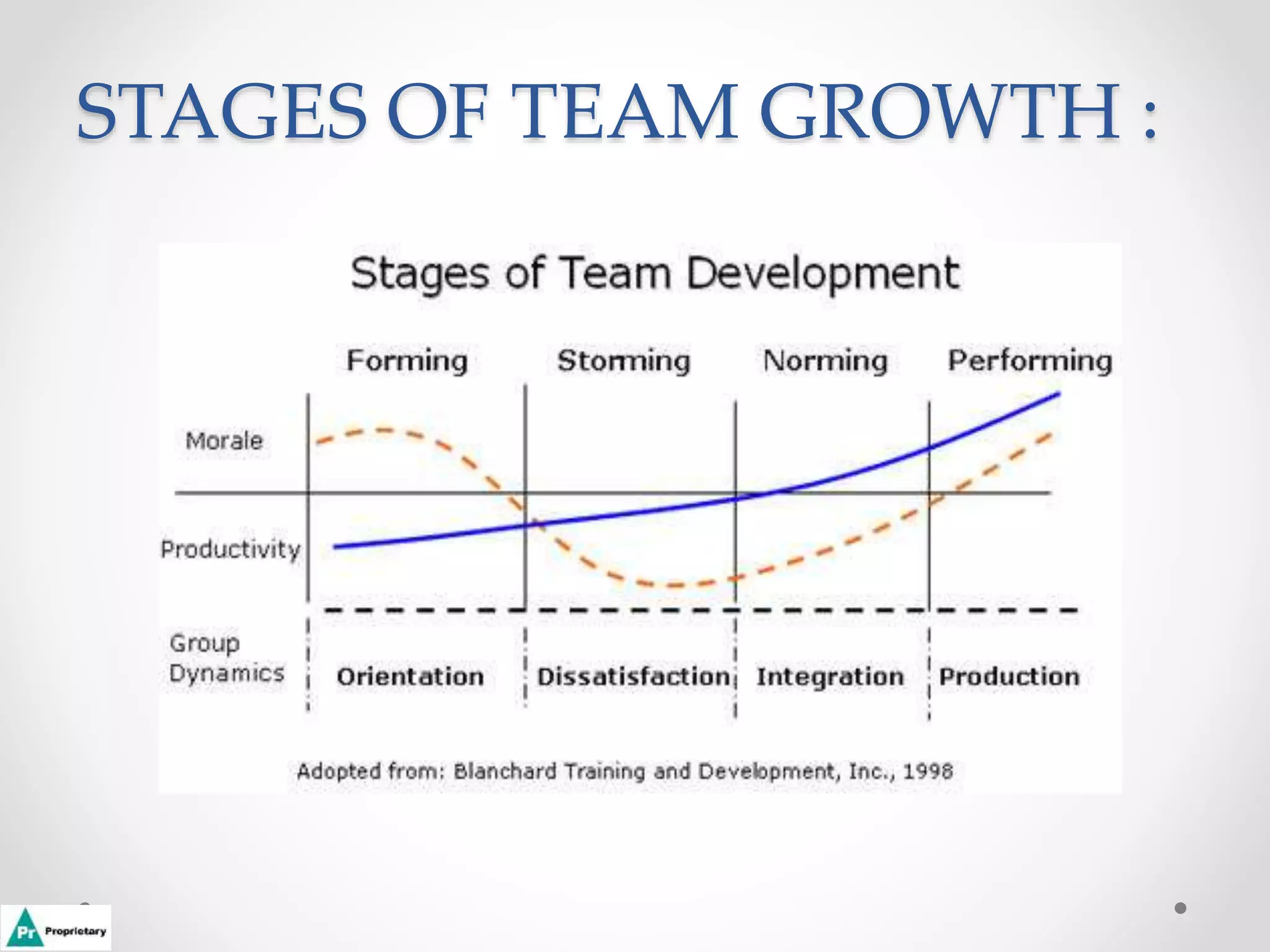
This document discusses how to transform a group into an effective team. It outlines Tuckman's stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. In the forming stage, team members learn goals and tasks but work independently. Storming involves conflict as opinions are formed. Norming resolves disagreements through cooperation. Performing teams work collaboratively toward common goals with high productivity. The document also provides tips for team meetings, such as starting on time and only allowing one conversation at a time.