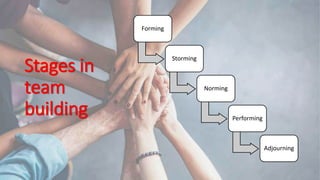
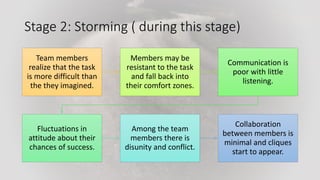
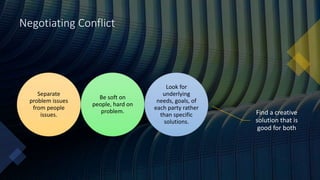
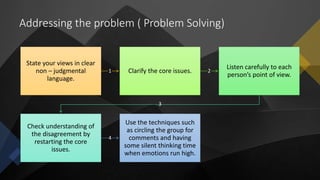
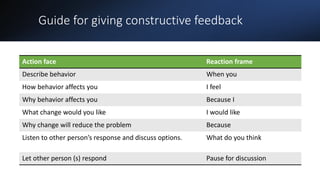
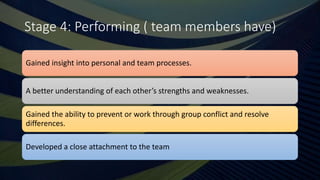
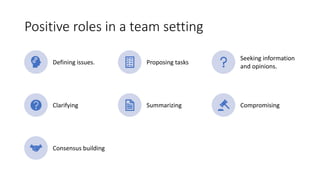
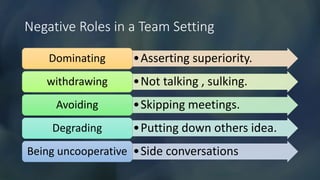
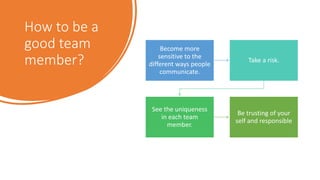
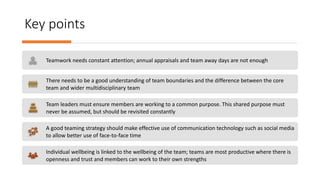
Teamwork is essential in modern workplaces. It requires complementary skills, commitment to common goals, and accountability. Effective teams have clearly defined roles, open communication, and resolve conflicts constructively. Nursing teams in particular rely on cooperation and coordination to provide high-quality patient care. Strategies like establishing shared goals, clear communication, and mutual respect help nursing teams function successfully.