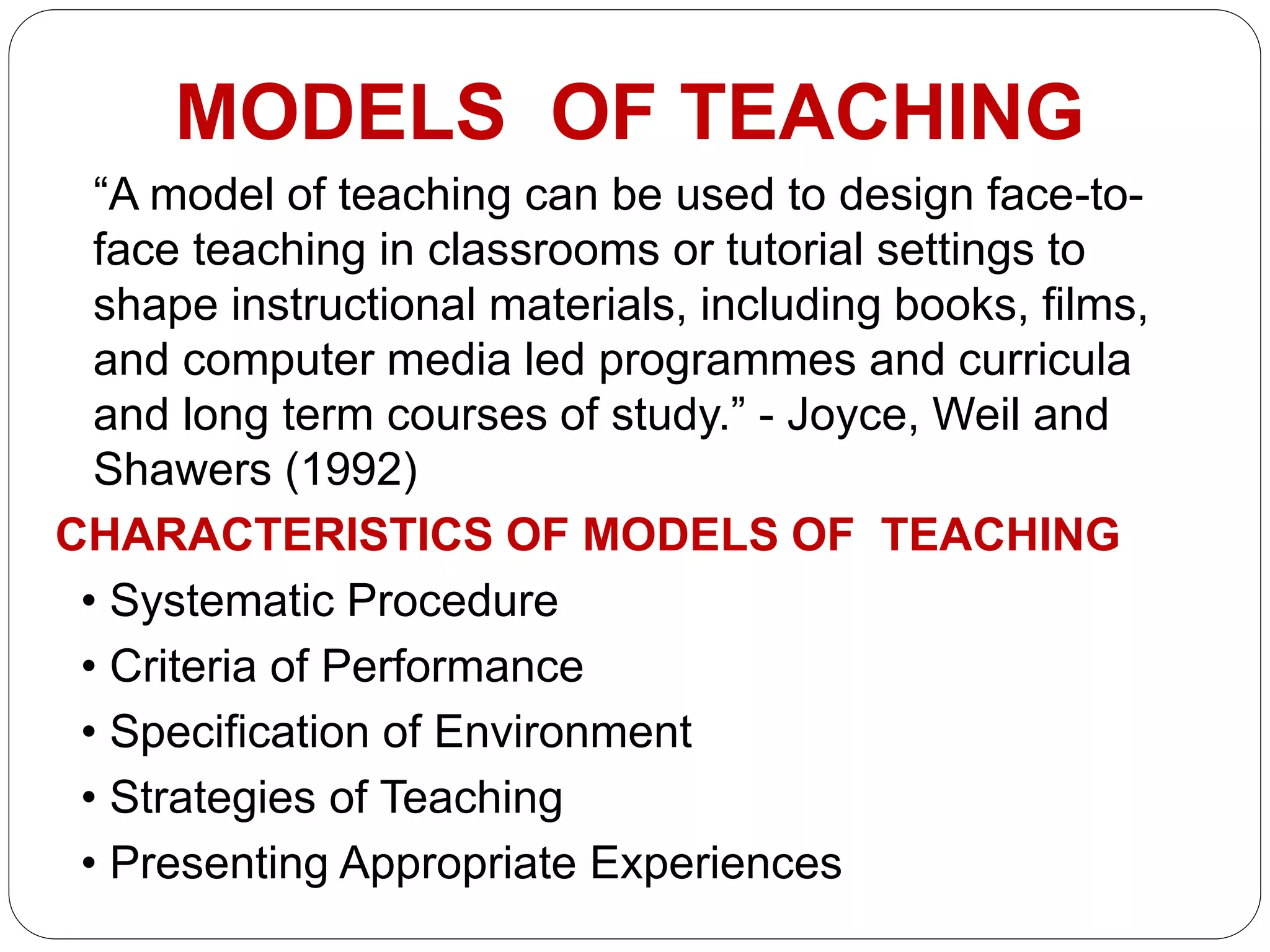
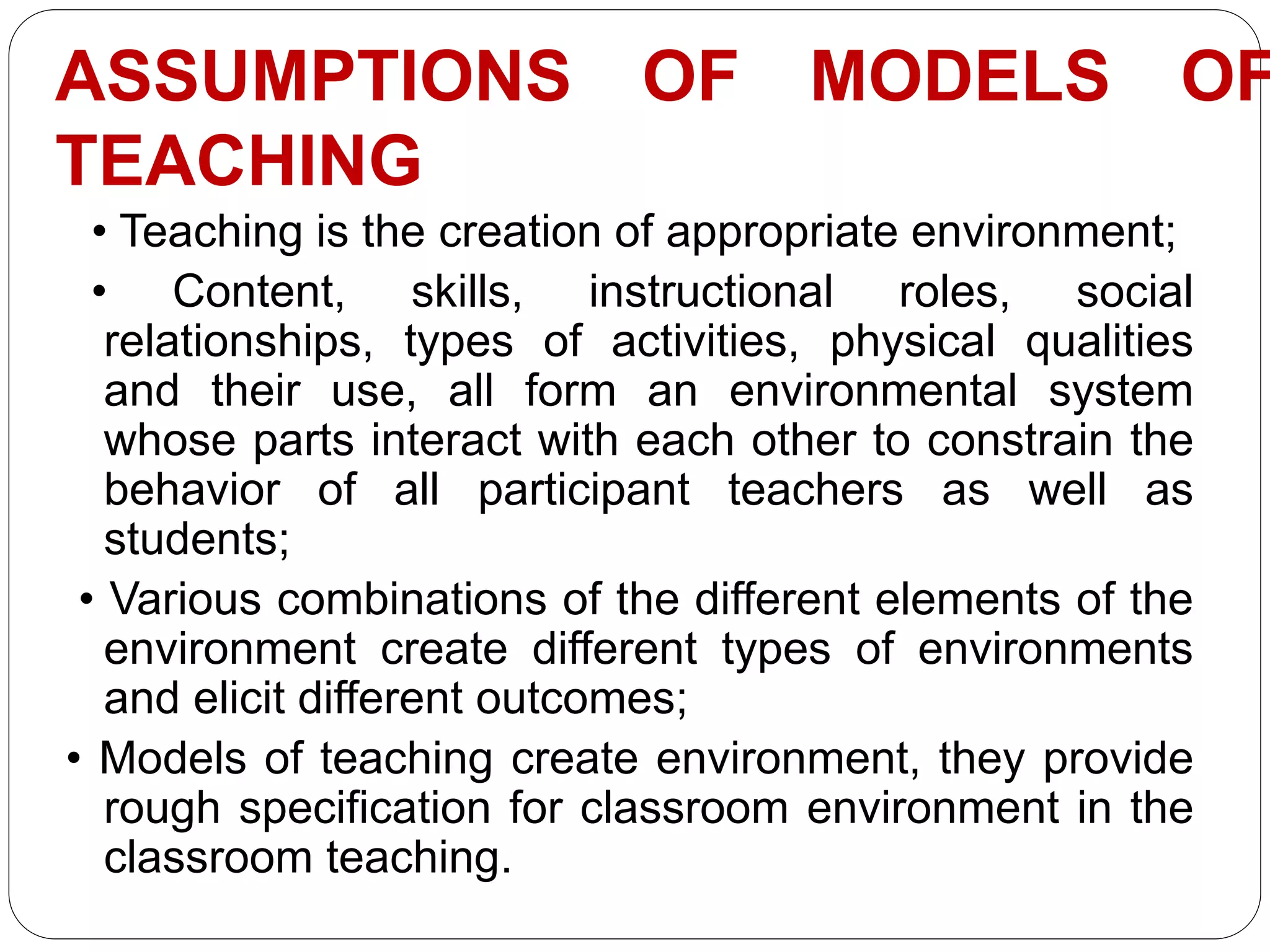
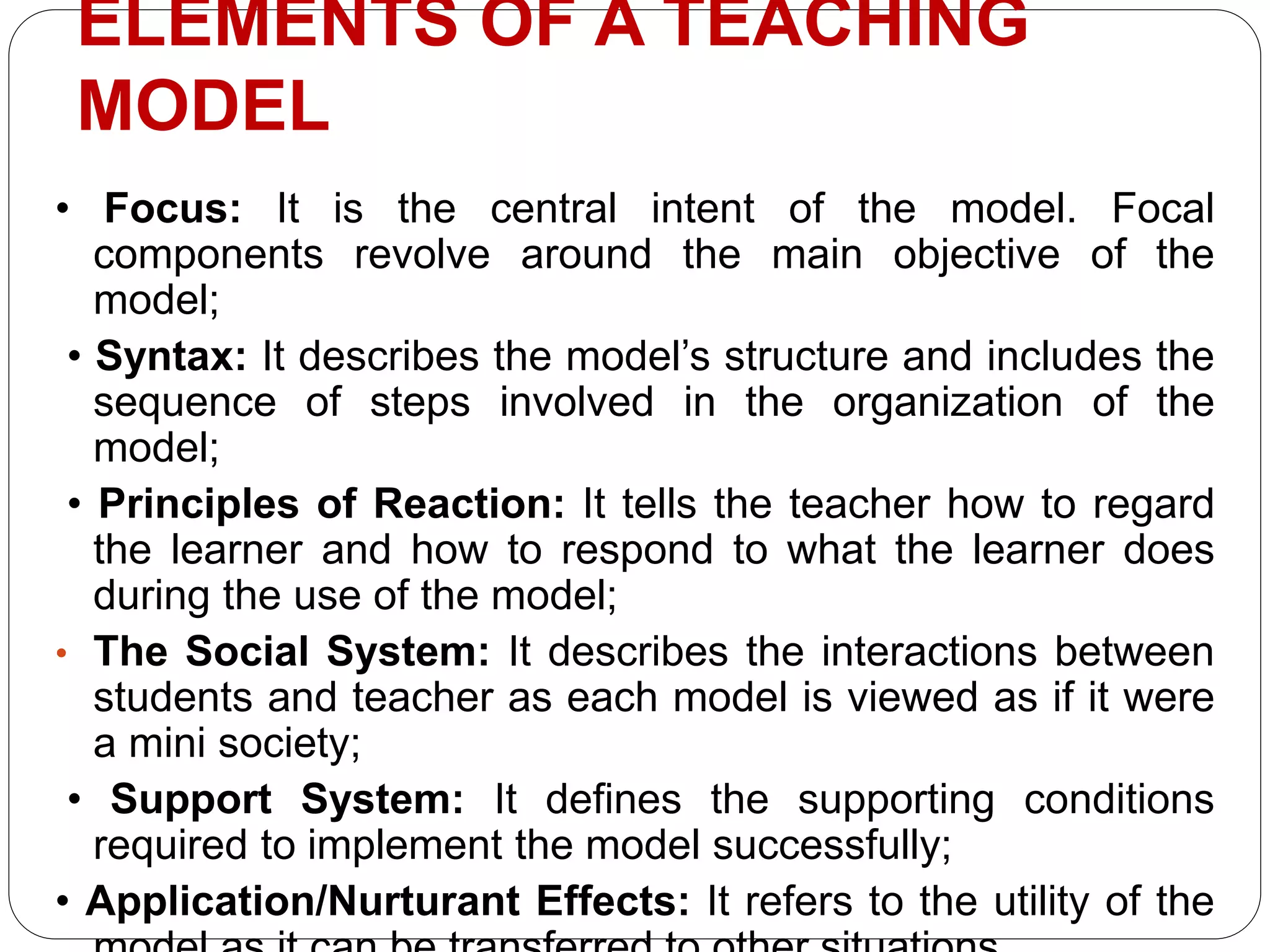
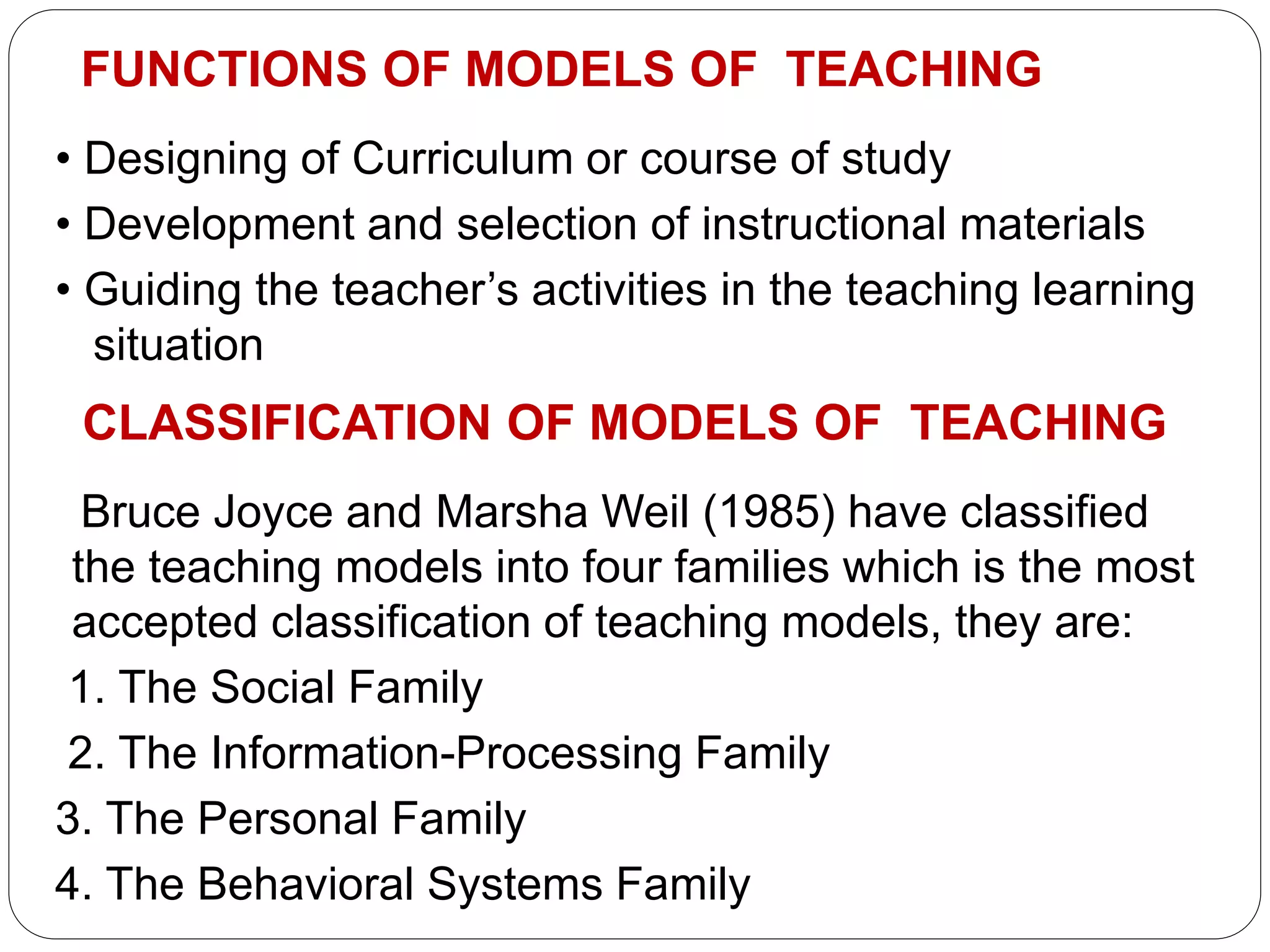
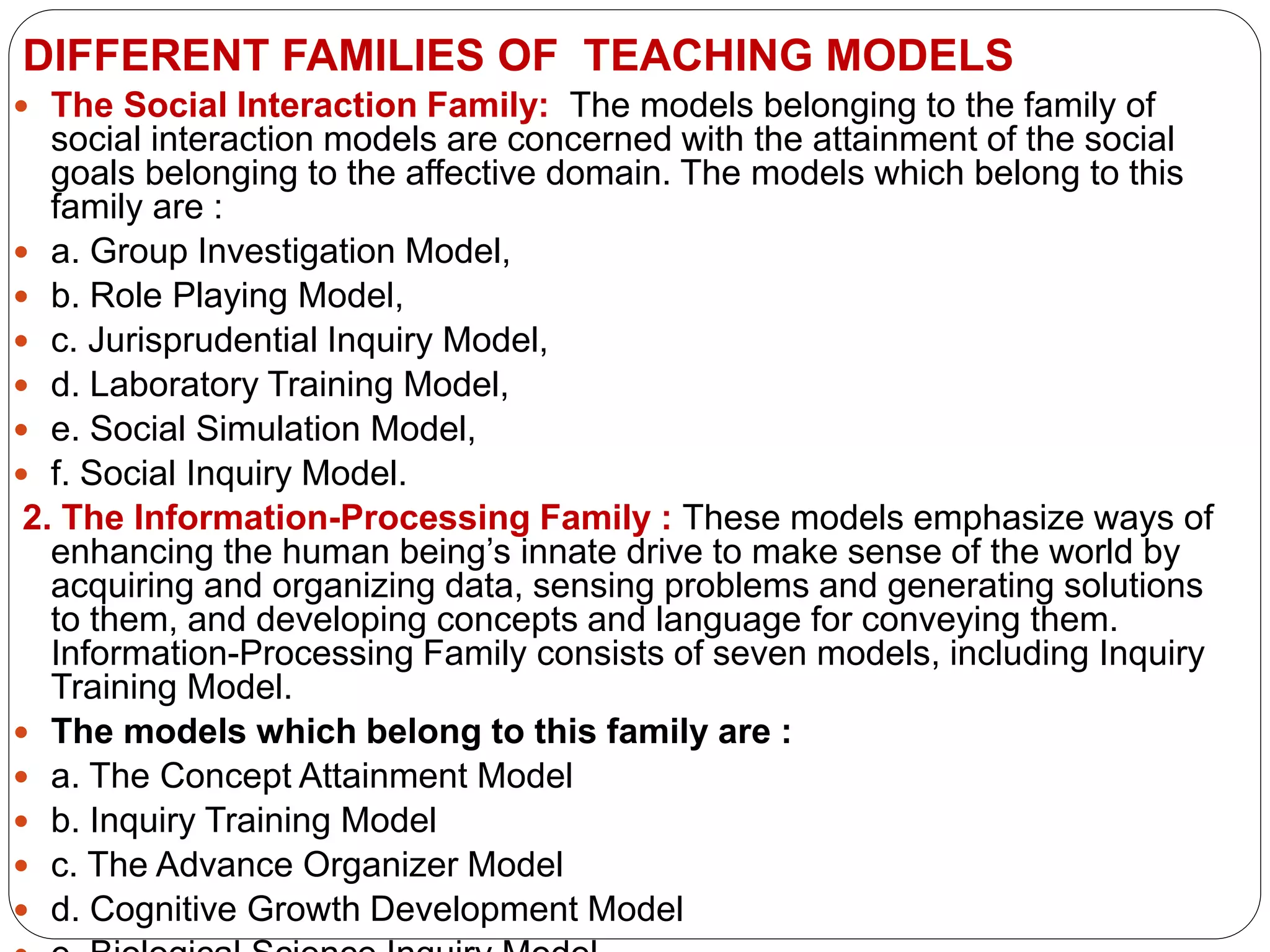
This document discusses models of teaching, which provide systematic procedures and criteria to design instruction. There are four main families of teaching models: social models that focus on social goals, information processing models that enhance understanding, personal models that develop selfhood, and behavioral models based on behaviorism. Effective models create an optimal learning environment, specify teacher and student roles, and can be used to design curriculum, materials, and guide teaching activities.