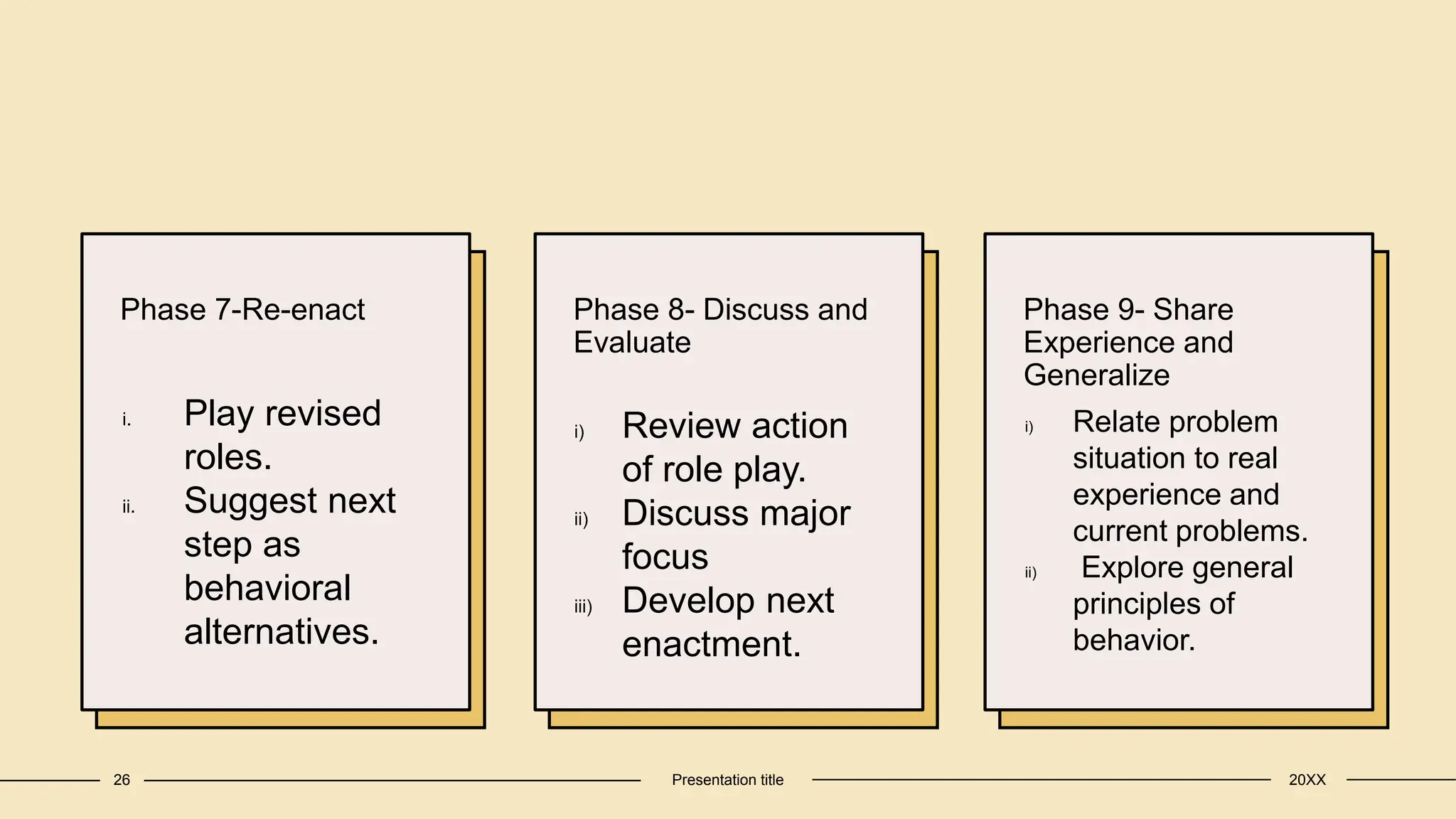
The document discusses teaching models, defined as structured plans used to guide instruction and shape curricula. It outlines key characteristics, assumptions, and sources of teaching models, as well as specific methods such as role-playing, which facilitates social understanding and problem-solving among students. Ultimately, these models aim to enhance the educational experience by fostering interaction, development of personal abilities, and critical thinking.