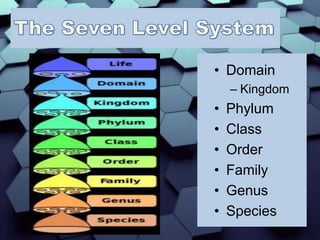
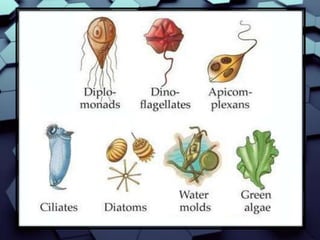
This document describes Carl Linnaeus' system for classifying living organisms into a taxonomic hierarchy consisting of Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species. It provides details on the three Domains of Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya, and describes key distinguishing characteristics used for classification such as cell structure, number of cells, mode of nutrition and habitat.