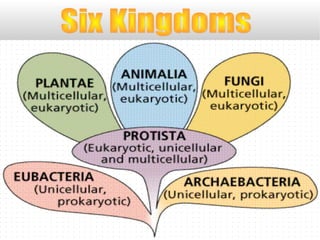
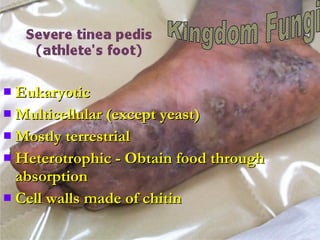
There are over 2 million known species of organisms that are classified into 6 major kingdoms. The document then provides details about the characteristics of each kingdom, including whether organisms are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, unicellular or multicellular, and how they obtain nutrients. It also discusses the scientific naming of species using binomial nomenclature with the genus and species names.