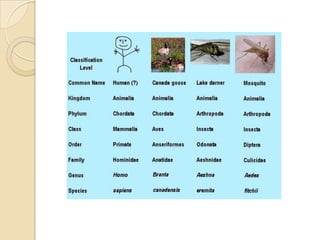
This document discusses the classification of living things. It explains that classification involves grouping organisms according to similarities. It outlines the modern 7-level classification system including kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species. The document also describes binomial nomenclature developed by Carolus Linnaeus, which uses a two-part scientific name for each organism. Finally, it discusses how taxonomic keys can be used to identify organisms based on physical characteristics.