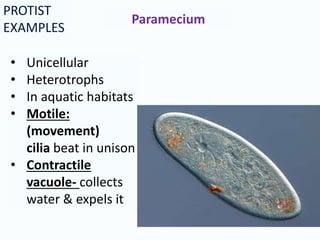
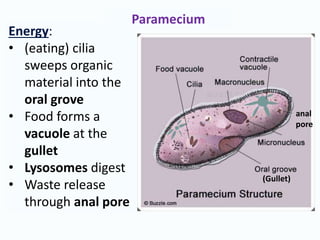
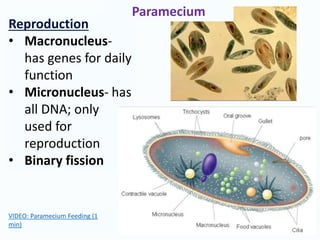
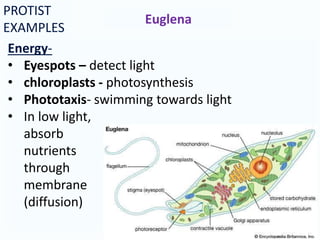
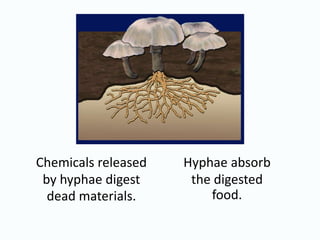
This document provides information about the kingdoms of life: Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. It summarizes key characteristics of each kingdom. Protists are eukaryotic microscopic organisms that can be single-celled or multi-cellular and obtain energy through photosynthesis or consuming other organisms. Fungi are usually unicellular but some are multicellular, and they are all heterotrophs that absorb nutrients. Plants are usually multicellular and autotrophic, obtaining energy through photosynthesis. Animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, obtaining nutrients by ingesting other organisms.