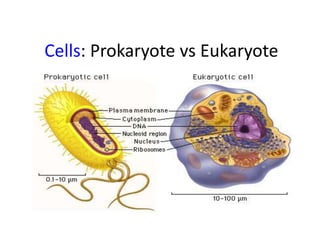
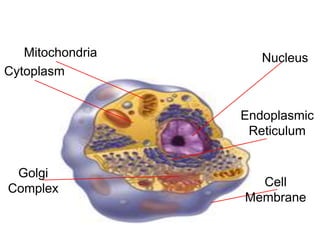
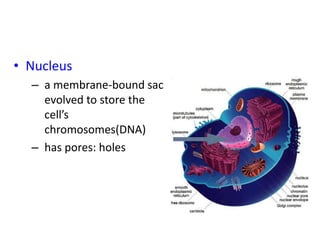
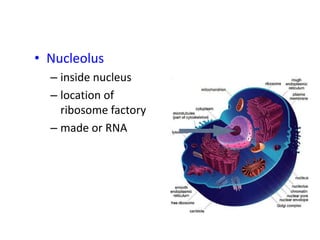
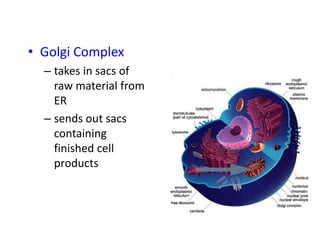
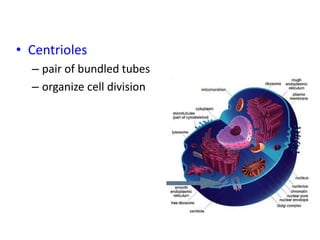
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells were the earliest life on Earth and lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells evolved later and have organelles within membranes. Key differences include prokaryotes being smaller, unicellular, and lacking a nucleus, while eukaryotes can be multicellular, have organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts, and contain DNA within the nucleus. Both share some basic components like the cell membrane but eukaryotes have a more complex internal structure adapted for specialized functions.