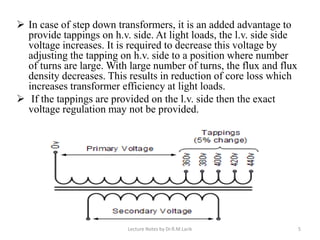
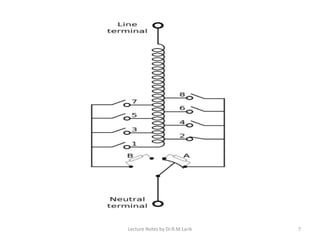
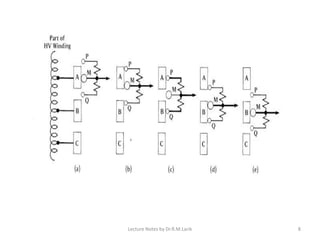
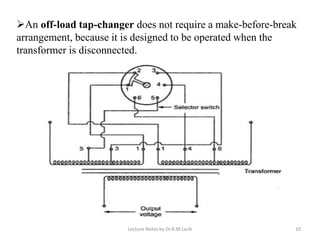
Tappings are provided on transformer windings to allow the voltage ratio and output voltage to be varied. This is done through a tap changer mechanism, which can be automatic or manual. Tap points are usually located on the high voltage winding due to the lower current, and to allow for finer voltage regulation. On-load tap changers must switch between taps without interrupting the load current, which is achieved through a make-before-break transition involving temporary resistances to limit short-circuit currents. Off-load tap changers can be simpler since the transformer is disconnected during operation. Tappings and tap changers thus provide a means of stepped voltage regulation on transformers.