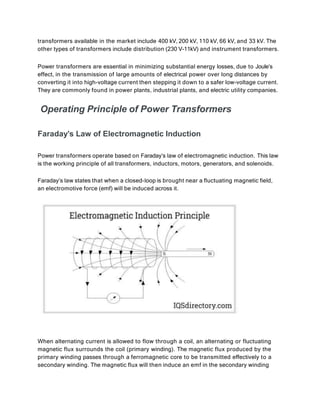
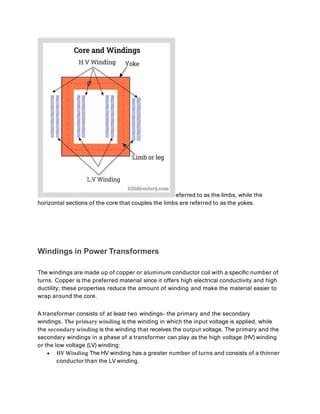
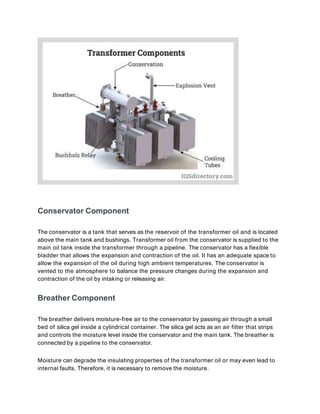
Power transformers are static devices used to transmit electrical power between circuits without changing frequency. They operate using electromagnetic induction and are used to step up or down transmission voltages. Power transformers have ratings between 33-400 kV and above 200 MVA. They are essential for minimizing energy losses during long distance power transmission by increasing voltage for transmission then decreasing it for distribution. Power transformers work by inducing an emf in the secondary winding through a fluctuating magnetic field produced in the primary winding according to Faraday's law of induction. The number of turns in each winding determines whether the transformer steps up or down the voltage. Key components include the core, windings, insulating materials, tap changers, bushings, tank, conservator, breather