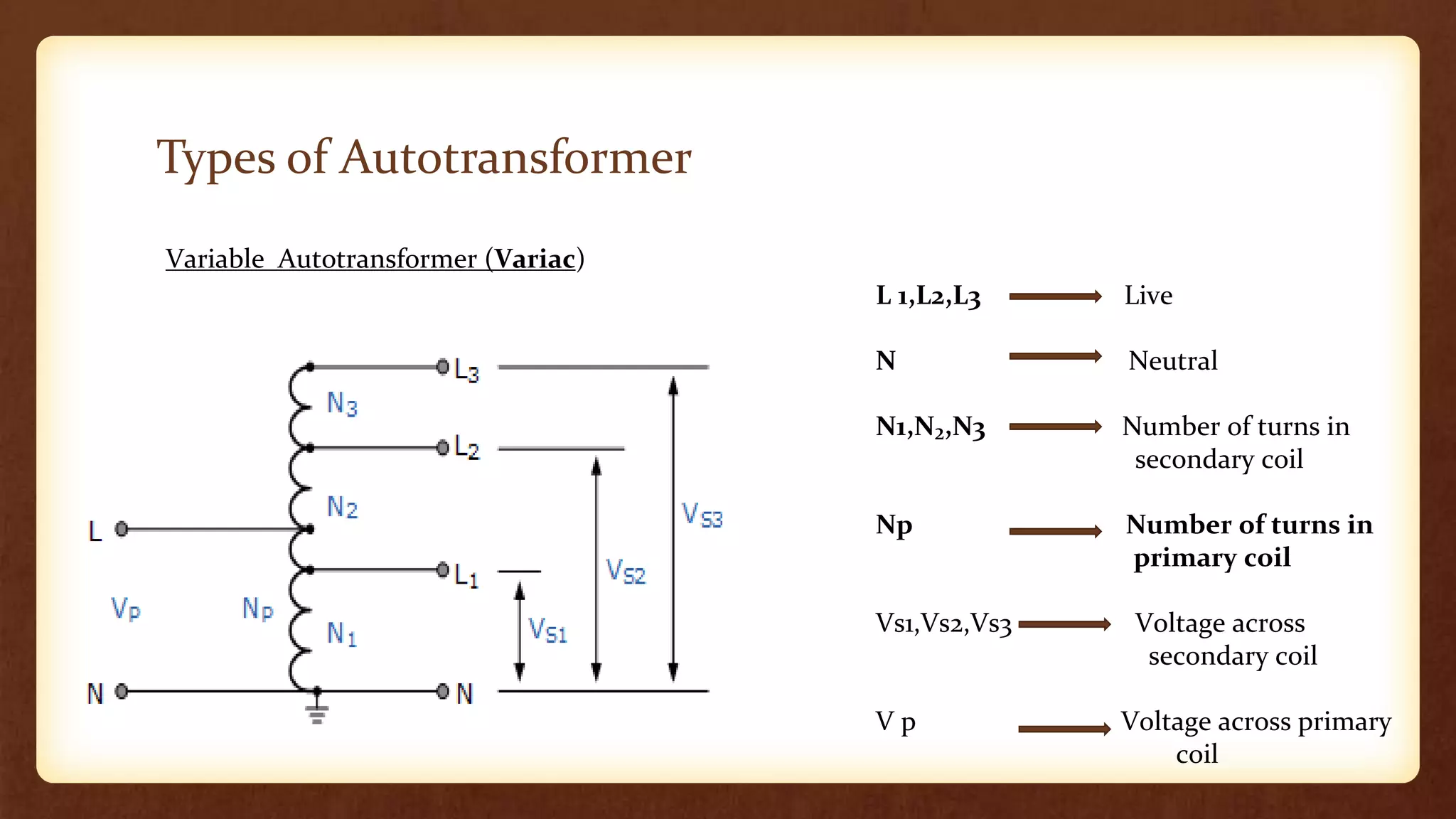
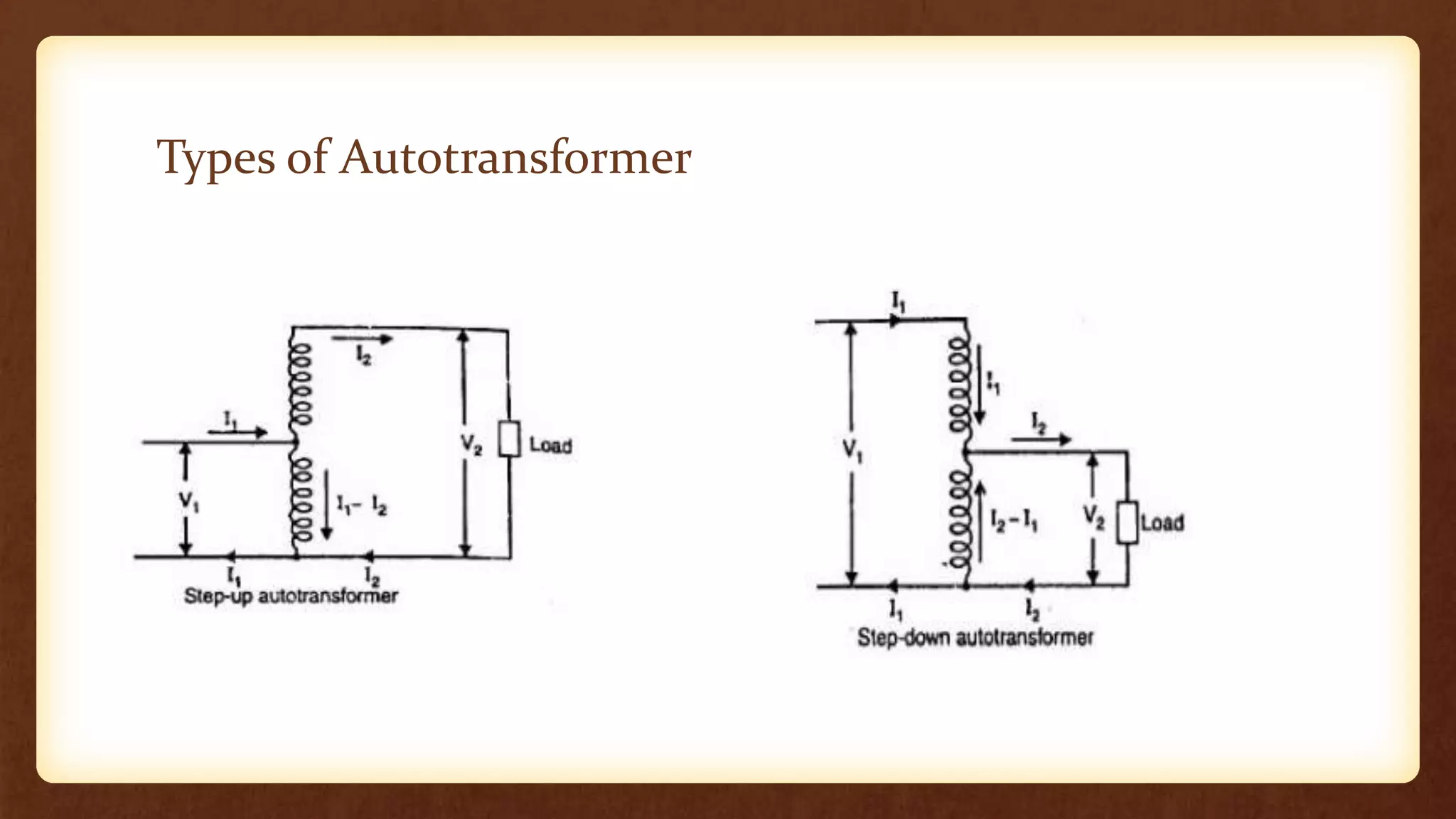
An autotransformer has a single winding that acts as both the primary and secondary winding. It uses a tapping mechanism to vary the number of turns for the secondary, which varies the output voltage while keeping it proportional to the input voltage. Autotransformers are more economical than two-winding transformers since they require less winding and core material. They are used for applications requiring a variable output voltage close to the input voltage, such as voltage regulation or motor starting. However, the load is not electrically isolated from the source like it is in a two-winding transformer.