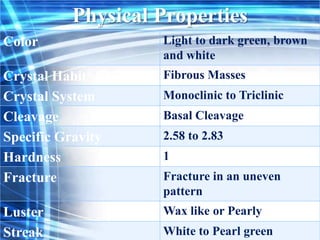
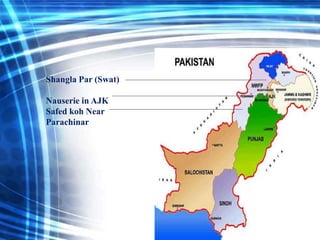
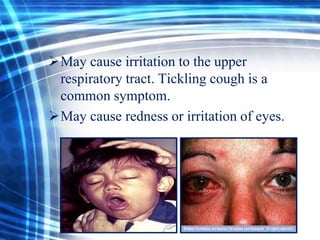
Talc is a soft mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, commonly used in industries such as paints, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals. Pakistan has significant reserves of high-quality talc, with major deposits located in regions like Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. However, talc is associated with health risks including respiratory diseases and potential cancer hazards due to its silica content and possible asbestos contamination.