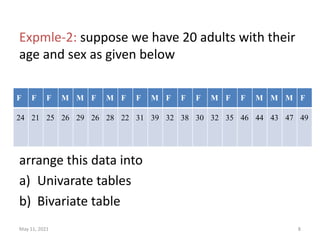
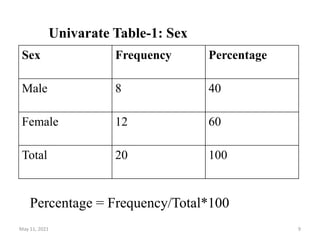
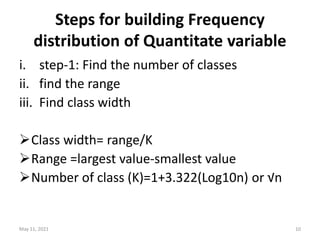
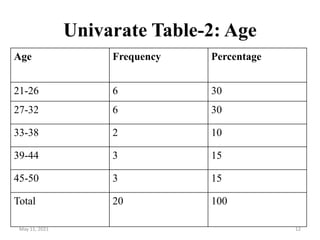
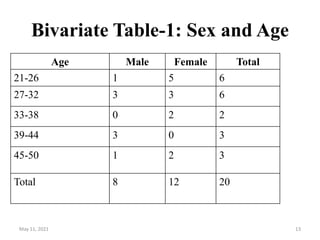
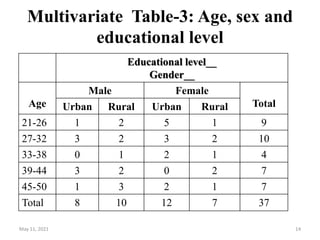
This document discusses different techniques for presenting data, including arrays, tables, and graphs. It provides examples of arranging data into ascending and descending order for array presentation. For tabular presentation, it describes the types and objectives of tables, and rules for tabulation. The document demonstrates arranging a sample dataset into univariate tables for sex and age, and a bivariate table crossing sex and age. Finally, it provides steps for building a frequency distribution of a quantitative variable and an example calculation.