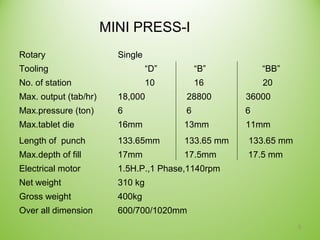
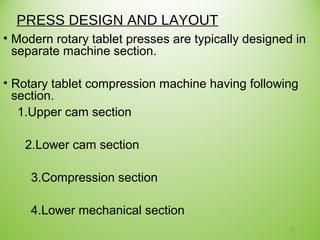
The document provides an extensive overview of tablet compression processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing, highlighting the importance of oral dosage forms like tablets. It covers various stages of tablet formation, including compression, decompression, and ejection, as well as details on rotary tablet press design and troubleshooting methods for common tablet production issues. Modern advancements in machinery are noted for increasing efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility in tablet production.