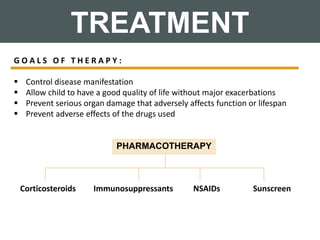
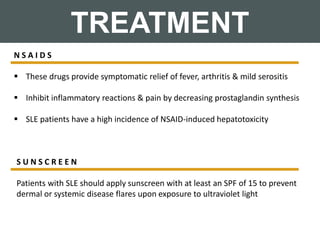
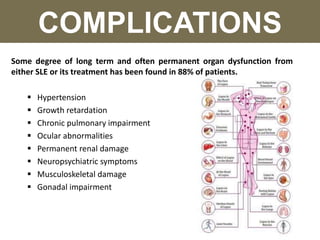
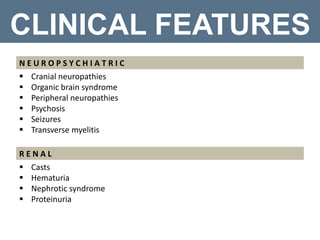
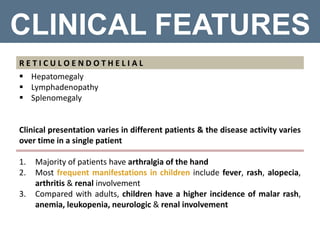
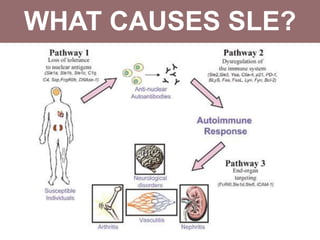
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects women of childbearing age but can also occur in children, characterized by diverse clinical manifestations and the production of autoantibodies. Diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical symptoms and laboratory criteria, with treatment aimed at controlling symptoms and preventing organ damage through medications such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. While the prognosis for SLE has improved significantly, complications can lead to long-term organ dysfunction in a substantial number of patients.



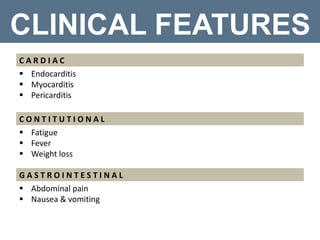











![DIAGNOSIS
I M M U N O L O G I C A L C R I T E R I A:
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) level above laboratory reference range
Anti-double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (dsDNA) antibody level above
laboratory reference range [or >2-fold the reference range if tested by
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)]
Anti-Smith (Anti-Sm): presence of antibody to Smith (Sm) nuclear antigen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiclupuserythematosus-180125101602/85/Systemic-lupus-erythematosus-SLE-23-320.jpg)
![DIAGNOSIS
I M M U N O L O G I C A L C R I T E R I A:
Antiphospholipid antibody positivity, as determined by:
o Positive test for lupus anticoagulant
o False-positive test result for rapid plasma reagin
o Medium- or high-titer anticardiolipin antibody level [Immunoglobulin A
(IgA), immunoglobulin G (IgG) or immunoglobulin M (IgM)]
o Positive test result for anti-B2-glycoprotein I [Immunoglobulin A (IgA),
immunoglobulin G (IgG) or immunoglobulin M (IgM)]
Low complement (C3, C4, or CH50)
Direct Coombs’ test (in the absence of hemolytic anemia)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiclupuserythematosus-180125101602/85/Systemic-lupus-erythematosus-SLE-24-320.jpg)