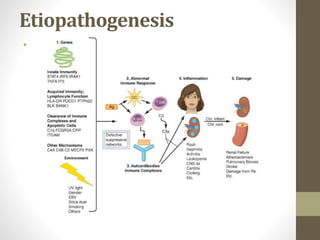
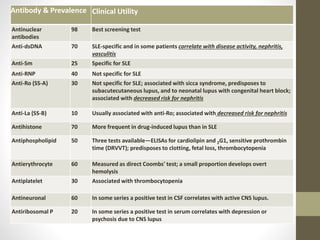
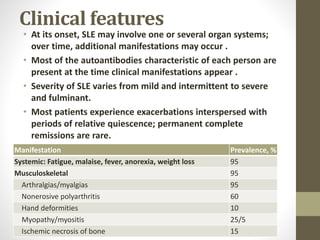
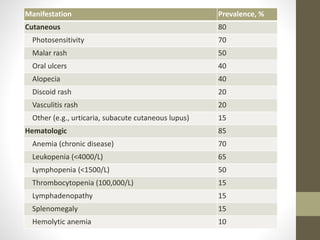
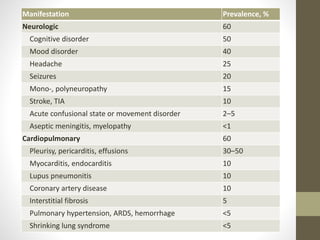
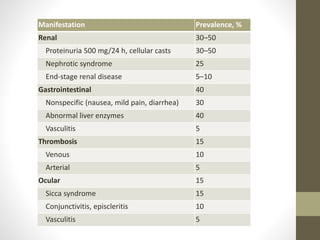
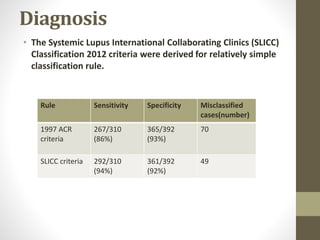
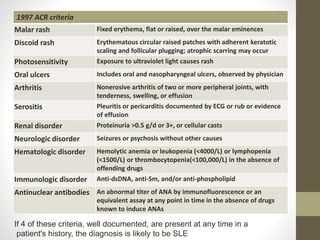
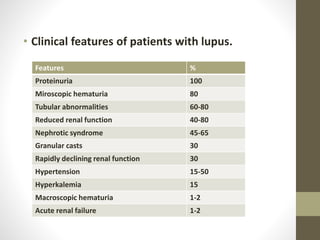
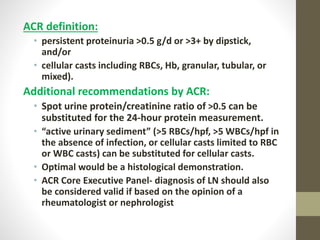
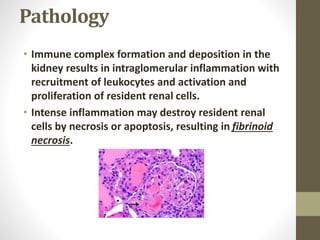
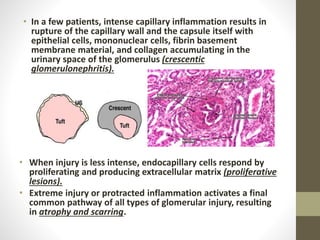
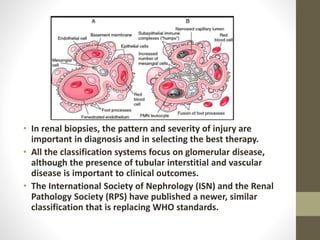
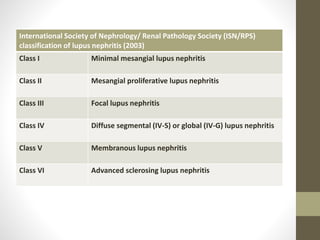
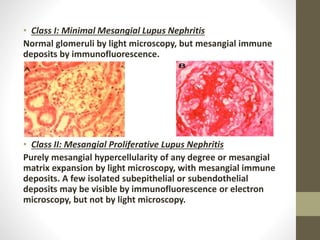
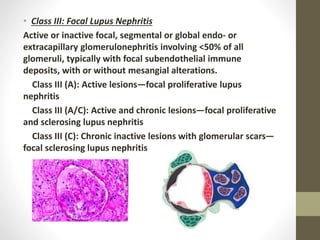
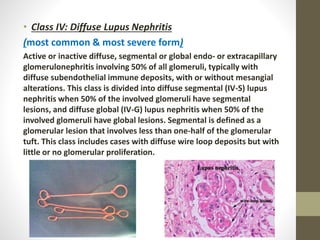
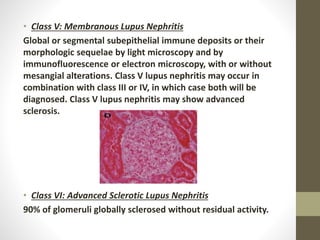
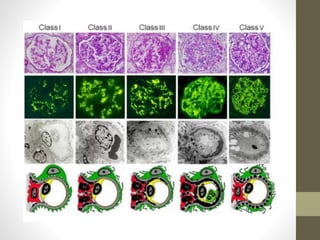
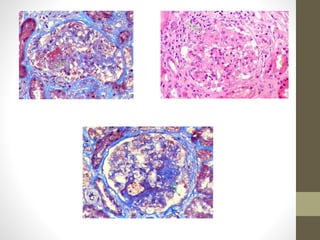
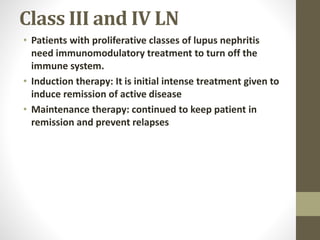
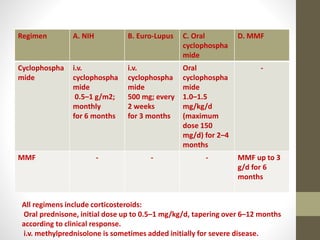
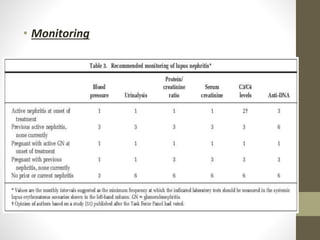
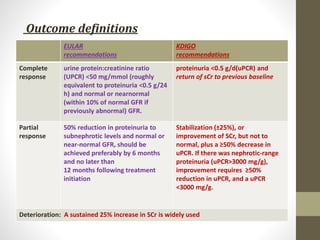
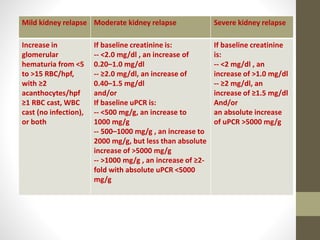
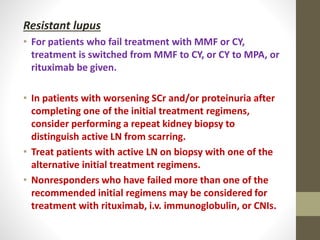
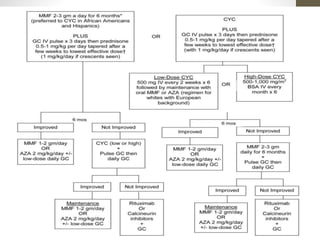
This document discusses lupus nephritis, a form of kidney involvement that can occur in up to 70% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. It provides guidelines for diagnosing and classifying lupus nephritis based on the presence of proteinuria, cellular casts in urine, and renal biopsy findings. Renal biopsy is important for classifying the type of glomerular inflammation and scarring according to the ISN/RPS classification system and for guiding treatment decisions. Left untreated, lupus nephritis can lead to end-stage renal disease.