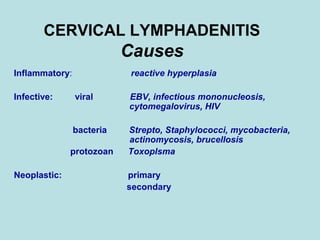
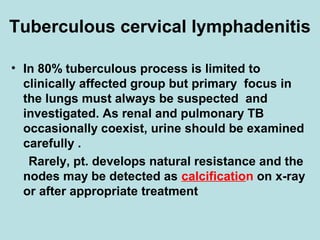
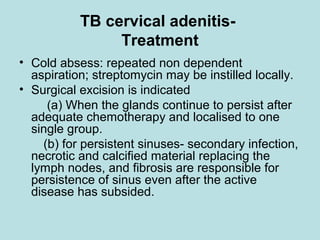
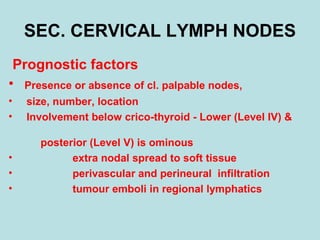
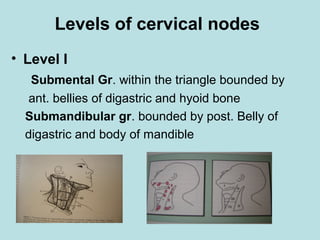
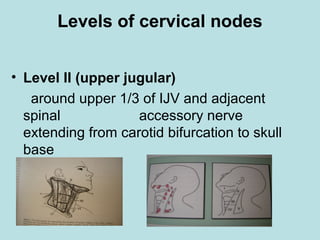
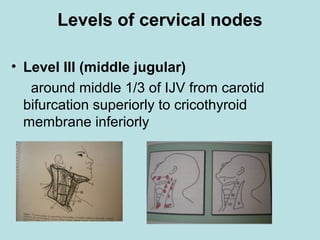
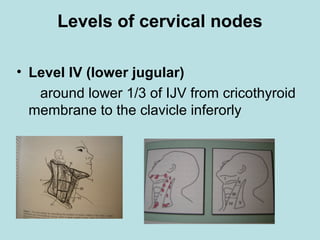
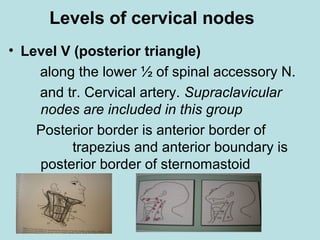
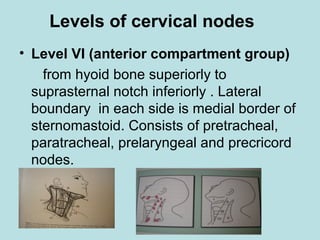
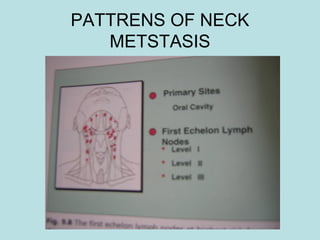
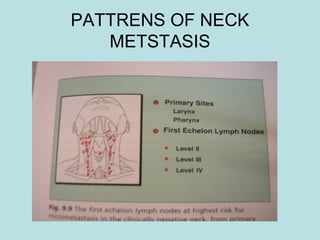
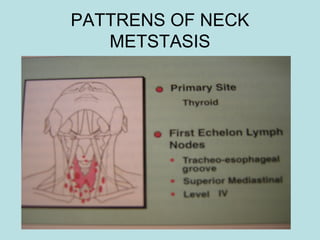
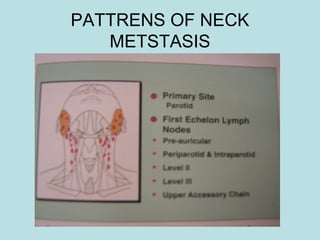
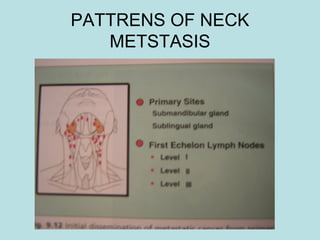
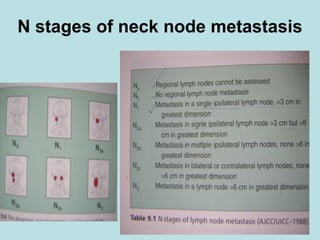
This document discusses cervical lymph nodes and lymphadenitis. It covers causes of cervical lymphadenitis including infectious, neoplastic, and tuberculous etiologies. It describes acute and chronic cervical lymphadenitis. Tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis is discussed in depth, covering pathology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Levels of cervical lymph nodes and patterns of neck metastasis are also outlined.