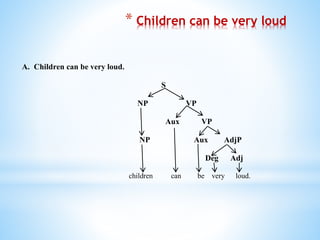
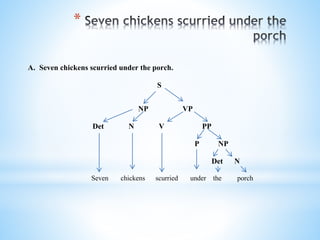
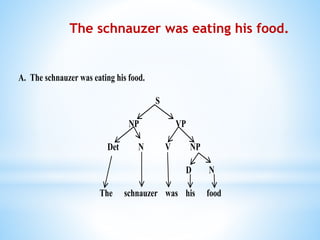
This document defines and categorizes the different parts of speech in syntax. It discusses lexical categories such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, determiners, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions and auxiliary verbs. It also examines phrasal categories including noun phrases, verb phrases, adjective phrases, adverbial phrases and prepositional phrases. Examples are provided to illustrate different parts of speech and how they are arranged to form sentences.