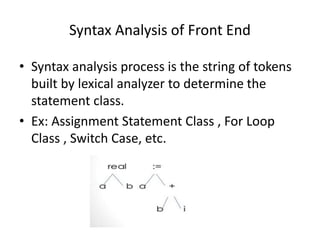
The front end of the Toy compiler performs lexical, syntax, and semantic analysis on source code. It constructs an intermediate code representation and stores analysis information in tables. The back end performs memory allocation, assigning addresses to identifiers, and code generation to produce assembly code. It handles issues like register allocation and determining instructions and addressing modes.