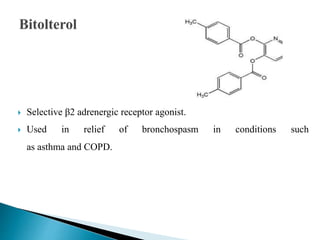
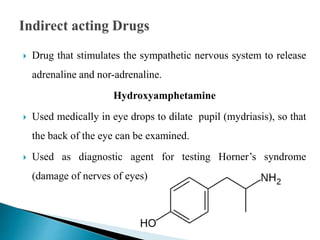
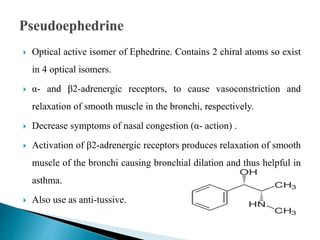
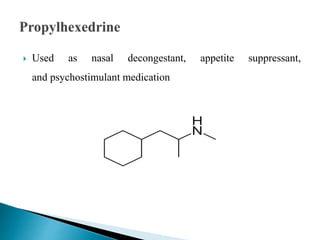
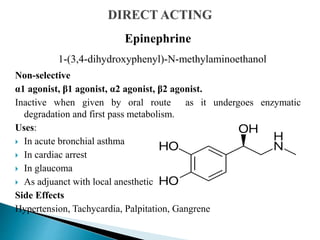
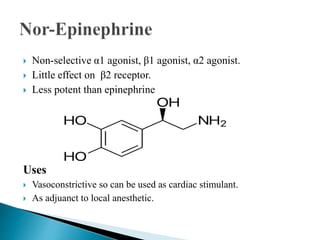
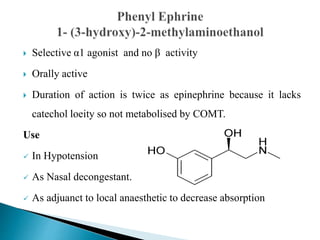
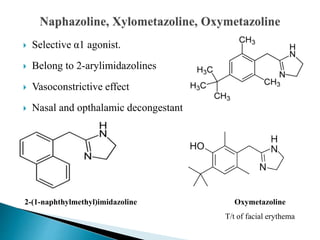
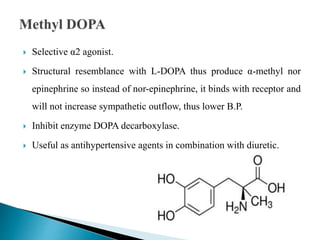
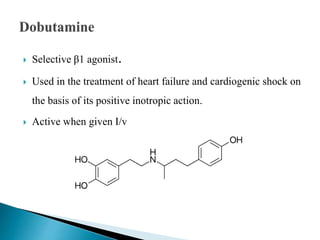
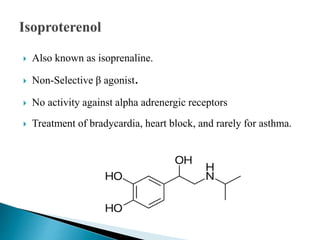
This document discusses various adrenergic drugs, including their mechanisms of action, receptor selectivity, uses, and side effects. Epinephrine is discussed as a non-selective adrenergic agonist used for conditions like asthma and cardiac arrest. Phenylephrine is an α1-selective agonist used for hypotension and as a decongestant. Clonidine is an α2-selective agonist used as an antihypertensive and for Tourette syndrome. Dobutamine is a selective β1 agonist used for heart failure. Albuterol is a selective β2 agonist used for asthma and COPD.

![ 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]-2-imidazoline
Selective α2 agonist.
Orally as well as I/v active
Interact specifically with α2 receptor and decrease sympathetic outflow.
Used as anti-hypertensive agent and in migraine also.
T/t of tourette syndrome (neuropsychiatric disorder with onset in childhood)
For clonidine, basicity of guanidine group is decreased to 8 because of
inductive and resonance effect of dichlorophenyl ring. Thus, it will exist in non-
ionized form required to enter CNS and thus produce sedative effect
(Premedication before surgery)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sympathomimeticdrugs-220517101745-1c1ffd4a/85/Sympathomimetic-Drugs-ppt-7-320.jpg)
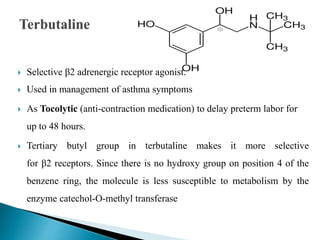
![ 2- t-butylamino-1-[(3-hdroxymethyl-4-hydroxy)phenyl]ethanol
Selective β2 adrenergic receptor agonist.
Used in management of asthma symptoms and COPD
Salbutamol has been used to treat acute hyperkalemia, as it stimulates
potassium flow into cells, thus lowering the potassium in the blood
As Tocolytic (anti-contraction medication)
Tertiary butyl group makes it more selective for β2 receptors. Since there is no
hydroxy group on position 4 of the benzene ring, the molecule is less
susceptible to metabolism by the enzyme catechol-O-methyl transferase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sympathomimeticdrugs-220517101745-1c1ffd4a/85/Sympathomimetic-Drugs-ppt-11-320.jpg)