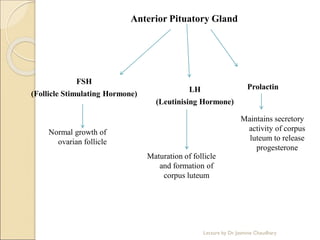
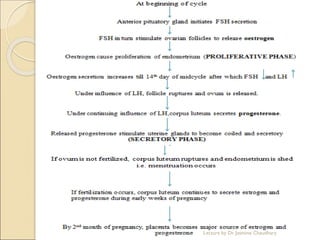
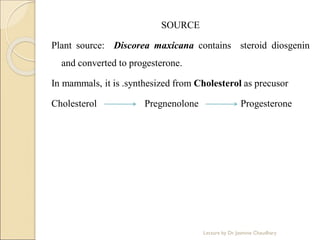
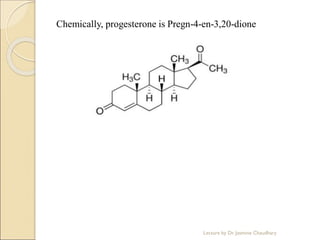
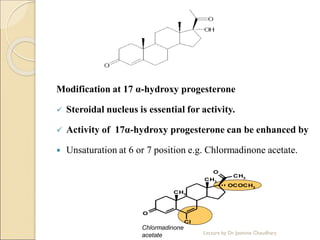
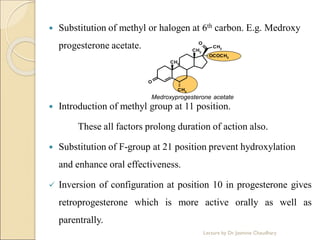
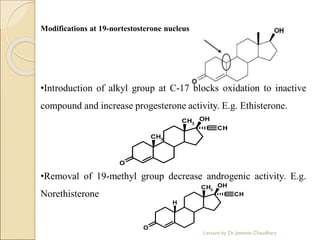
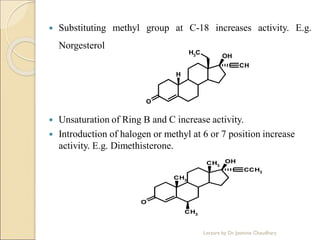
The document discusses progesterone, a hormone secreted by the corpus luteum and placenta that prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains pregnancy. It is synthesized from cholesterol and has various synthetic derivatives that were developed due to its degradation in the liver. These derivatives include 17α-hydroxy progesterone, 19-nortestosterone, and others created by modifying these structures. Progesterone and its derivatives have various uses including preventing abortion and supporting pregnancy, as well as side effects like nausea.