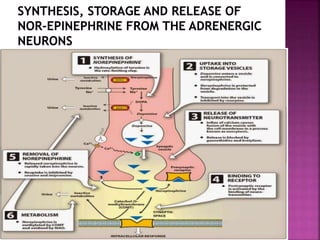
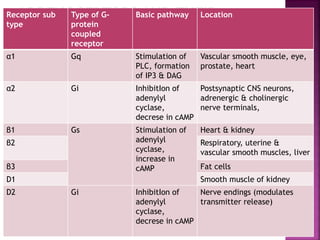
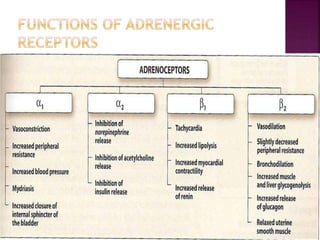
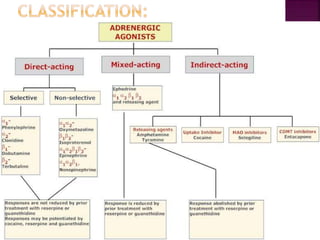
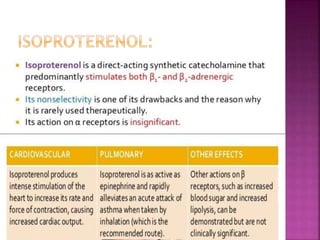
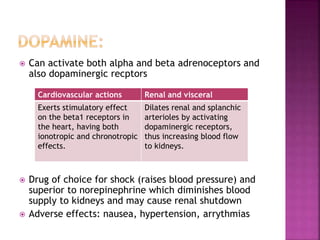
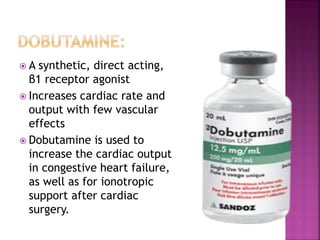
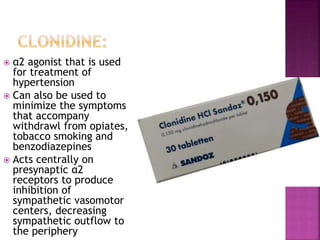
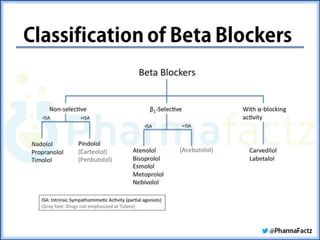
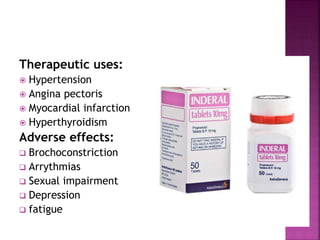
The document summarizes the sympathetic nervous system and adrenergic receptors and their ligands. It describes the key neurotransmitter norepinephrine and its receptors (alpha and beta). It then discusses various adrenergic drugs including agonists like epinephrine, norepinephrine, isoproterenol, and antagonists/blockers like phenoxybenzamine, phentolamine, prazosin and their mechanisms and uses.



























![ Phenoxybenzamine is nonselective, linking covalently
to both α1 and α2 receptors
Actions:
Cardiovascular effects: By blocking α receptors,
phenoxybenzamine causes decreased peripheral
resistance. The decreased peripheral resistance
provokes a reflex tachycardia. Furthermore, the
ability to block α2 receptors in the heart can
contribute to an increased cardiac output. [Note:
These receptors when blocked will result in more
norepinephrine release, which stimulates β receptors
on the heart to increase cardiac output]. Thus, the
drug has been unsuccessful in maintaining lowered
blood pressure in hypertension and has been
discontinued for this purpose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completessns-161211165112/85/adrenergic-agonists-antagonists-38-320.jpg)










![ stimulate the β receptor to which they are bound,
yet they inhibit stimulation by the more potent
catecholamines. The result of these opposing actions
is a much diminished effect on cardiac rate and
cardiac output compared to that of β-blockers
without ISA.
Decreased metabolic effects: Blockers with ISA
minimize the disturbances of lipid and carbohydrate
metabolism that are seen with other β-blockers.
Therapeutic use in hypertension: β-Blockers with
ISA are effective in hypertensive patients with
moderate bradycardia, because a further decrease in
heart rate is less pronounced with these drugs. [Note:
The b blockers with ISA are not used as anti-
arrhythmic or anti-anginal agents due to their partial
agonist effect.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completessns-161211165112/85/adrenergic-agonists-antagonists-52-320.jpg)
![ Therapeutic use in hypertension: Labetalol is
useful for treating the elderly or black
hypertensive patient. [Note: In general, black
hypertensive patients are not well controlled
with β-blockers.] Labetalol may be employed as
an alternative to methyldopa in the treatment of
pregnancy induced hypertension.
Adverse effects: Orthostatic hypotension and
dizziness are associated with α1 blockade.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completessns-161211165112/85/adrenergic-agonists-antagonists-54-320.jpg)
