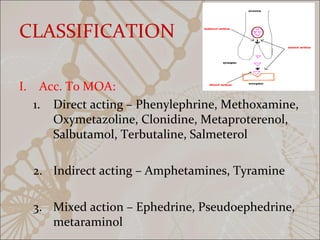
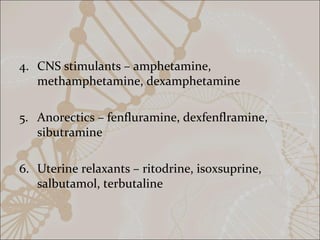
This document summarizes non-catecholamine drugs. It defines them as compounds lacking catechol hydroxyl groups and notes their longer half-lives, increased lipid solubility, and oral effectiveness compared to catecholamines. The document then classifies non-catecholamines by their mechanism of action and therapeutic uses. Examples of different types of non-catecholamines are provided, including their mechanisms, effects, and uses. Key non-catecholamines discussed include phenylephrine, methoxamine, ephedrine, amphetamines, pseudoephedrine, and beta-agonists.