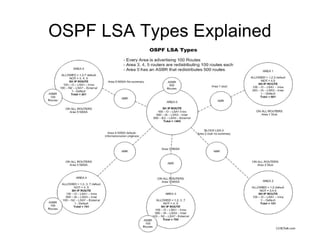
This document discusses the different LSA (Link State Advertisement) types in OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) networking. It explains that LSA types 1 and 2 are intra-area and do not leave the area, while type 3 are inter-area and describe routes outside the area. LSA types 5 and 7 describe redistributed routes from other protocols into an OSPF area, with type 5 generated by ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) and type 7 by ASBR within a NSSA (Not-So-Stubby Area).