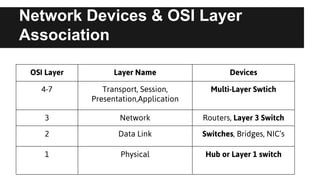
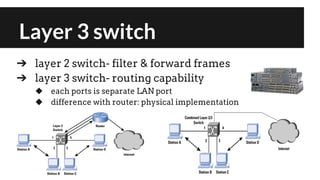
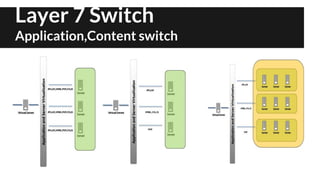
The document provides an overview of network switching, categorizing various types of switches including layer 1 to layer 7 switches, and their functions within network infrastructure. It describes the characteristics and operational differences of each switch type, such as port mirroring and error-checking, as well as their associations with OSI layers. The conclusion highlights the increasing complexity and functionality of these devices in network management.