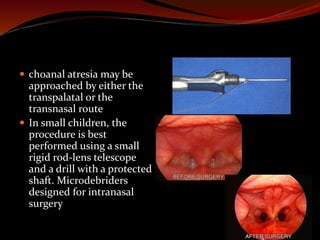
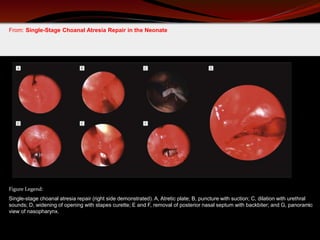
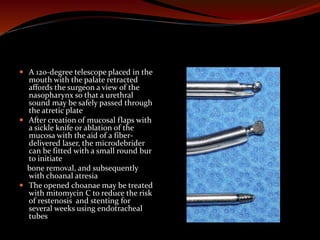
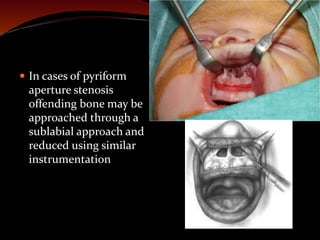
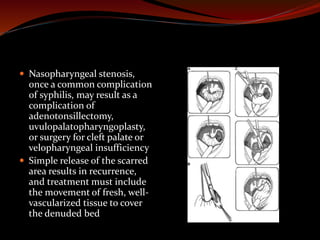
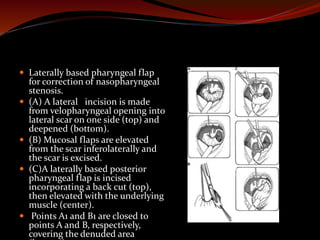
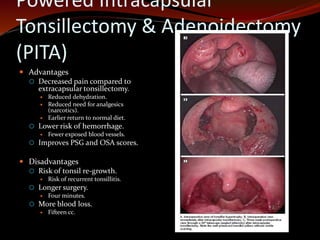
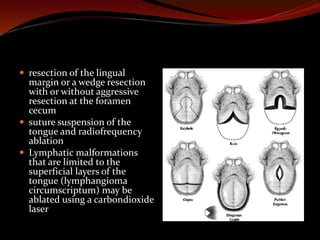
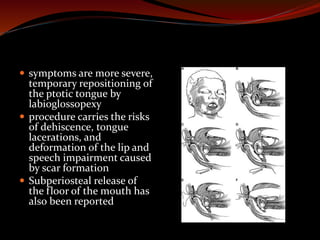
The document discusses various treatments for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It describes three main types of treatment: behavioral, devices, and surgery. Adenotonsillectomy is considered the first-line surgical treatment, while other options include craniofacial surgery and tracheostomy. It provides details on evaluating severity, nonsurgical management options, surgical techniques for conditions like choanal atresia and macroglossia, and the use of distraction osteogenesis for midface and mandibular abnormalities.

















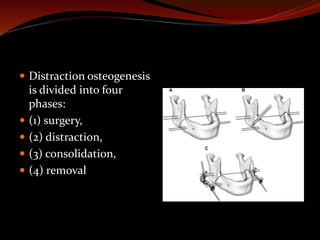
![Distraction osteogenesis
First described in 1969 by Ilizarov and Lediaev [116] in
the treatment of limb length discrepancies, osteotomy
with distraction of bone is now widely accepted as the
procedure of choice in the early management of airway
obstruction caused by craniofacial disproportion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surgeryforpaediatricsleepapnea-160608173823/85/Surgery-for-paediatric-sleep-apnea-28-320.jpg)