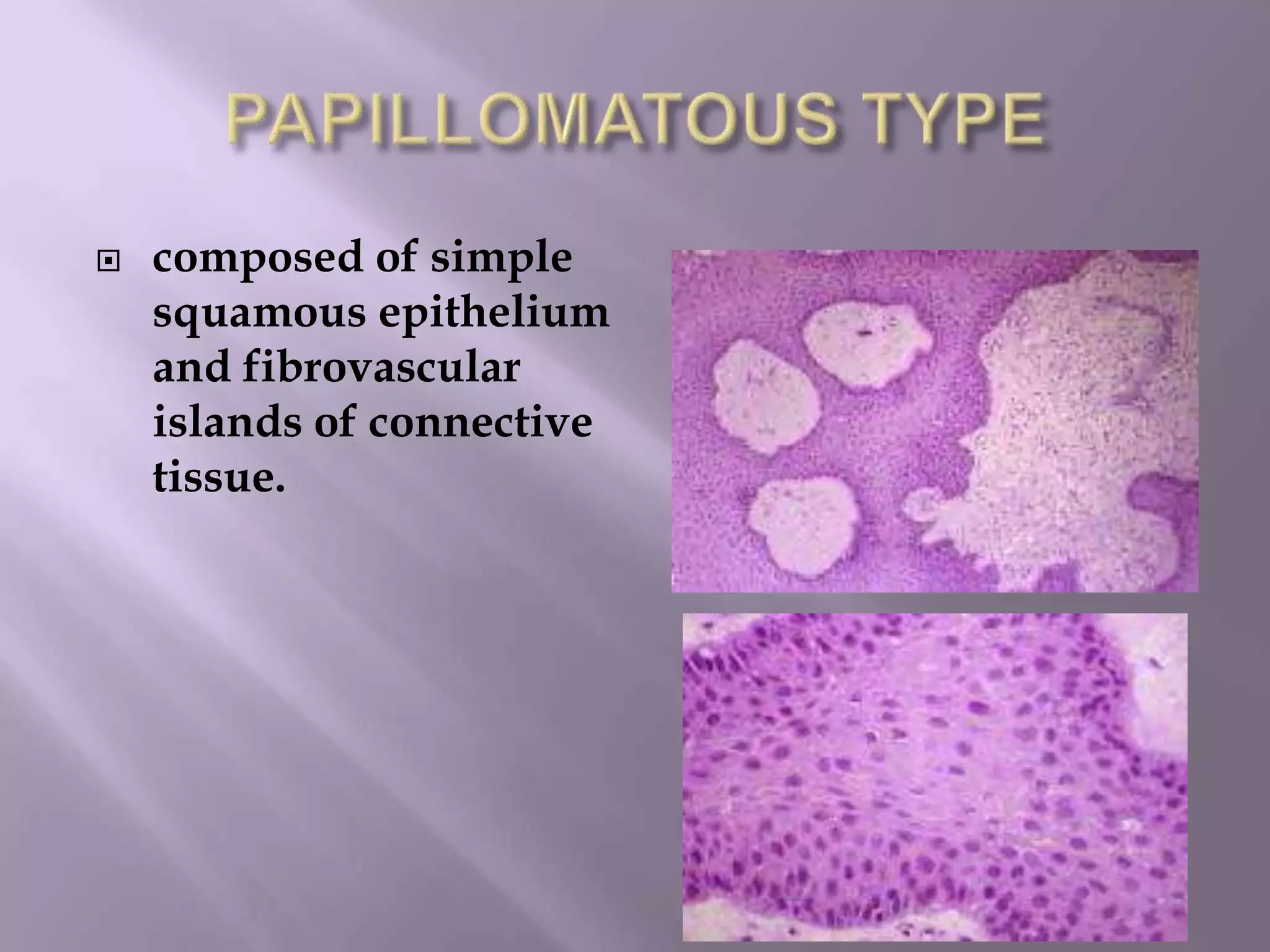
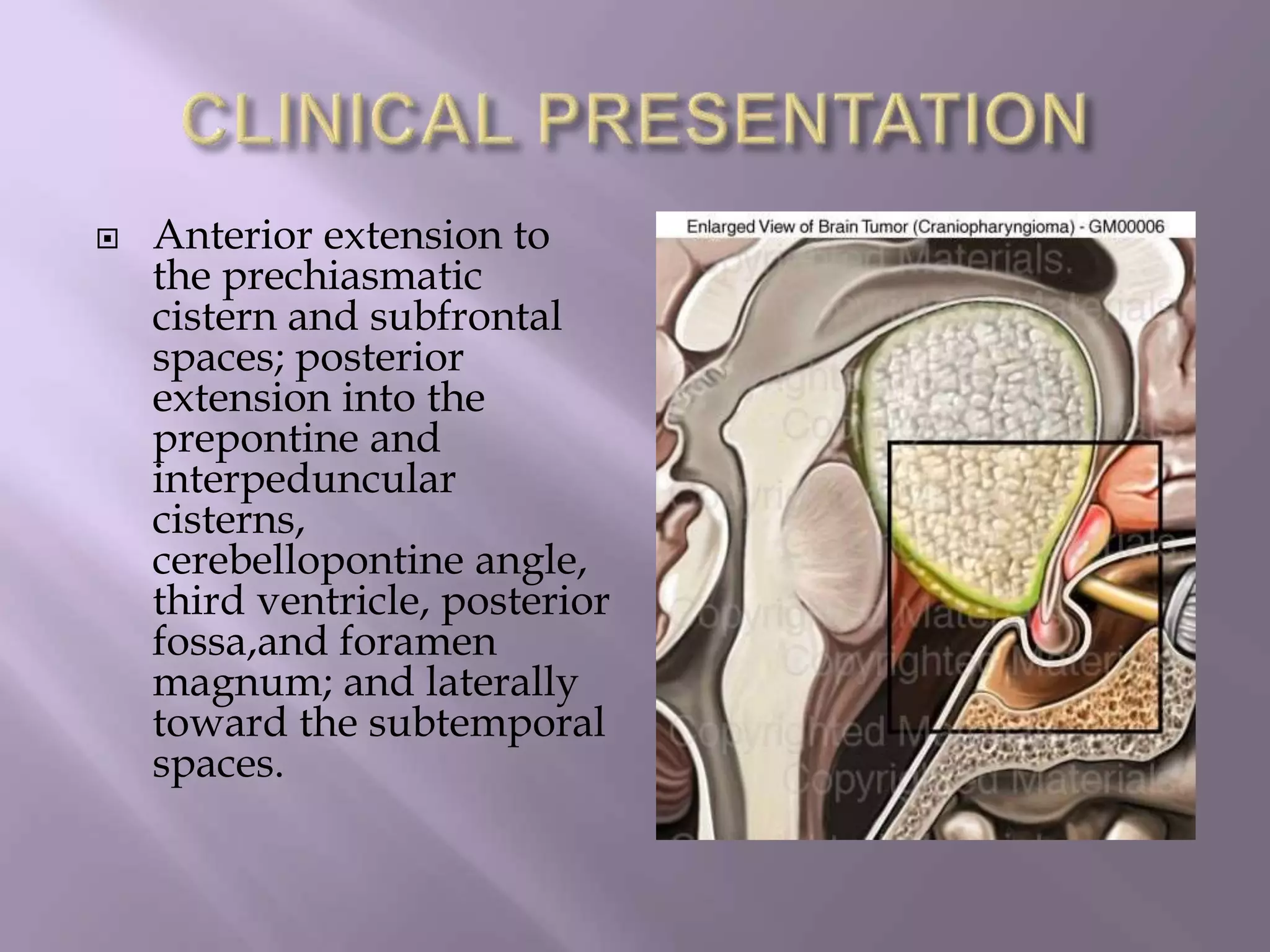
Craniopharyngioma is a rare, slow-growing benign tumor that arises from remnants of the craniopharyngeal duct near the pituitary gland. It occurs most commonly in children aged 5-10 years and adults aged 50-60 years. Histologically, there are two main types: adamantinous and papillary. Adamantinous craniopharyngiomas are more common in children, often calcified and cystic. Papillary craniopharyngiomas occur in older patients and are typically solid. Patients present with headaches, visual symptoms, and hormonal imbalances. On imaging, craniopharyngiomas are often suprasellar but can extend throughout the ventricular system