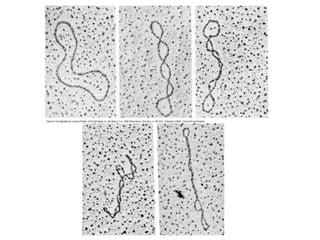
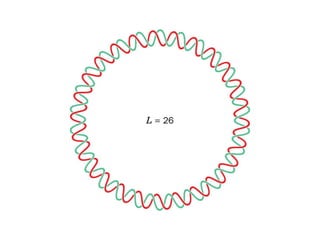
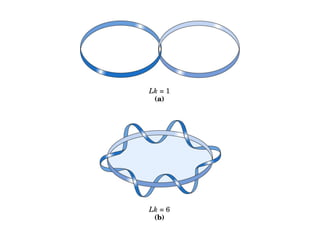
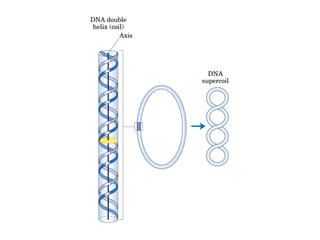
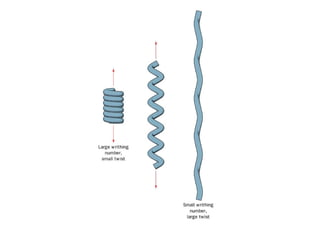
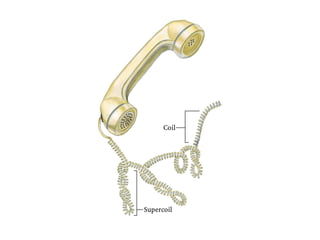
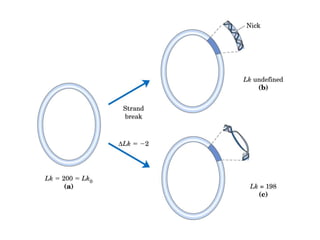
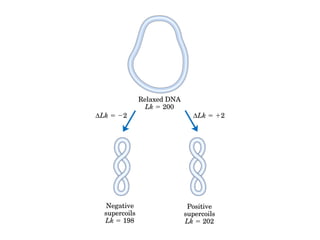
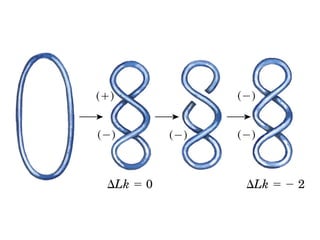
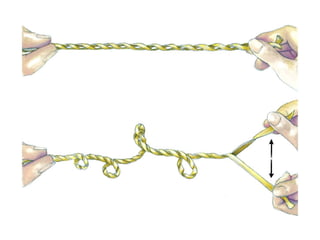
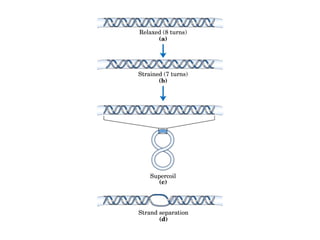
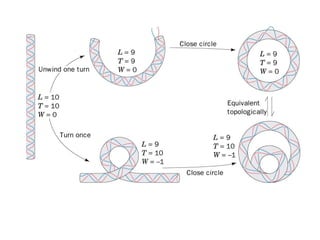
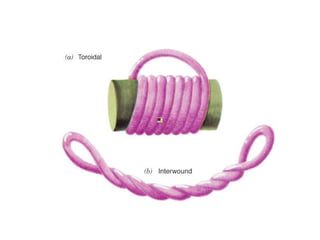
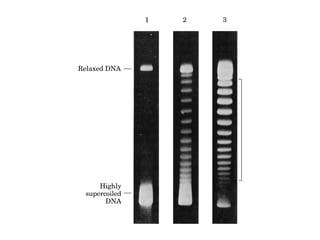
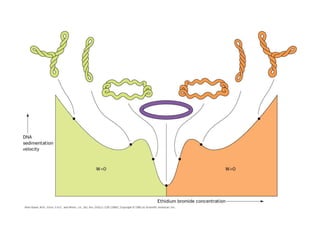
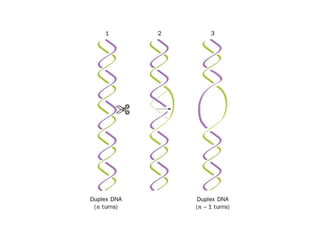
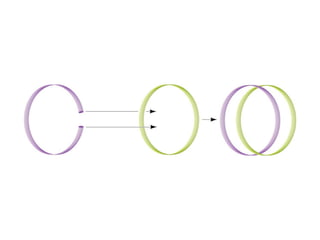
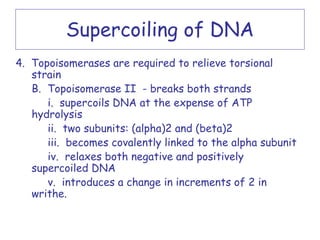
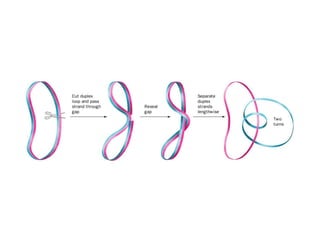
DNA supercoiling occurs when the DNA double helix is over- or under-wound, known as positive and negative supercoiling respectively. The degree of supercoiling is numerically expressed using the linking number which accounts for twists and writhes in the DNA helix. Topoisomerases are enzymes that relieve torsional strain in supercoiled DNA by introducing nicks in one or both strands, allowing the strands to pass through one another and change the linking number.